Oximetry-supported self-management for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: mixed method feasibility pilot project
- PMID: 26503028
- PMCID: PMC4624181
- DOI: 10.1186/s12913-015-1135-2
Oximetry-supported self-management for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: mixed method feasibility pilot project
Abstract
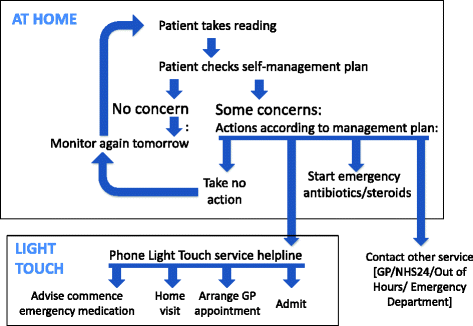
Background: Pulse oximetry could potentially contribute to self-monitoring. NHS Lothian's 'Light Touch' service provided COPD patients with a self-management plan based on symptoms and oximetry. The service was overseen (though not actively monitored) by respiratory-trained community teams who were contactable by a telephone helpline. We aimed to assess the feasibility, perceived utility and impact of the 'Light Touch' service.
Methods: A before-and-after assessment of St George's Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ), Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS) and use of healthcare resources during the 6-month feasibility study compared to the previous corresponding 6-months. Paired semi-structured interviews with patients at baseline and 6-months, interviews with managers and a focus group of professionals explored perceptions of the service and self-management. Transcripts were coded, and analysed thematically.
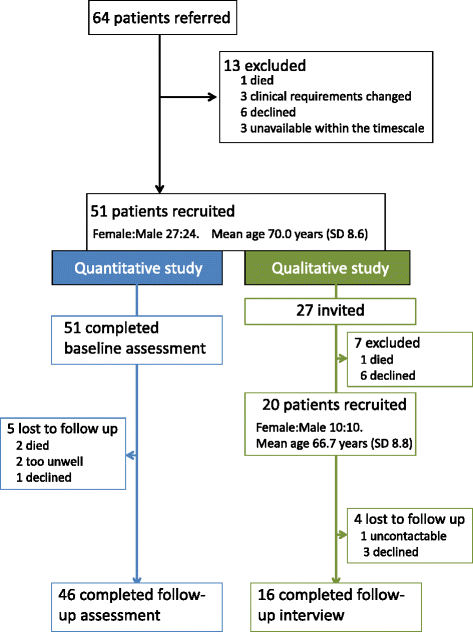
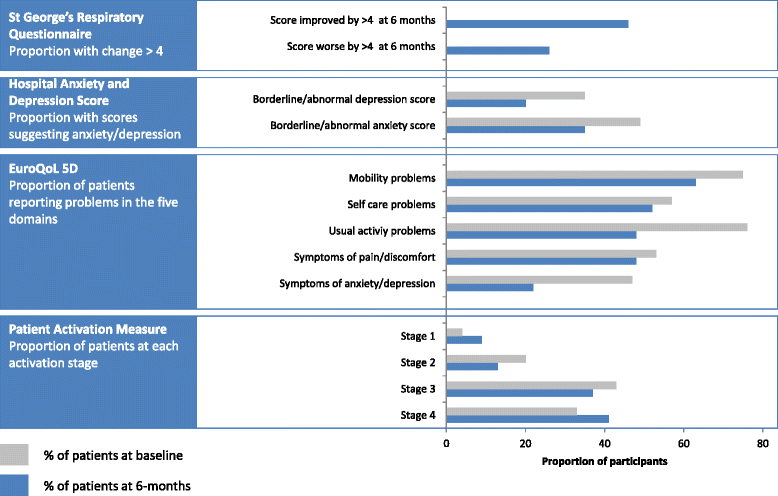
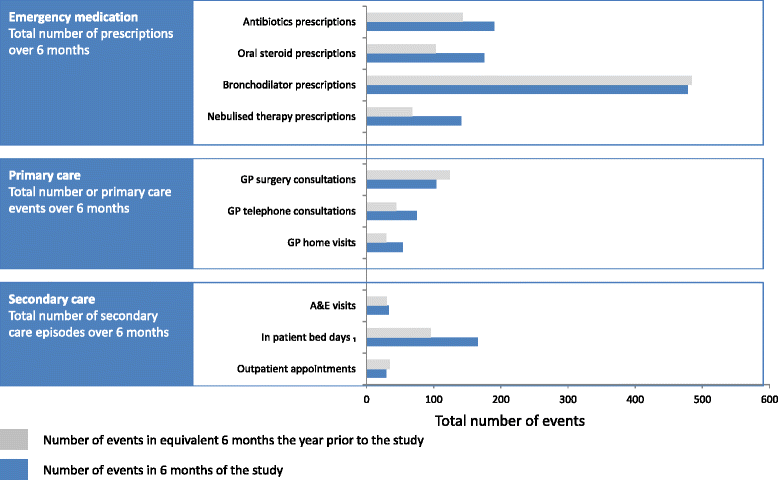
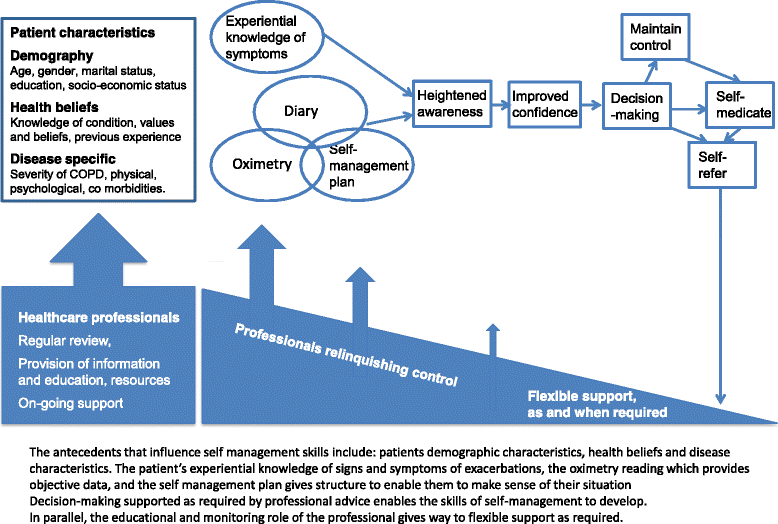
Results: We recruited 51 participants (mean age 69.7 years (SD 8.4); 21 (46%) male). 46 participants completed quantitative follow up (2 died, 2 were unwell, 1 refused). SGRQ: 21 (46%) participants improved by 4 or more (the minimum important difference); 12 (26%) deteriorated by 4 or more. HADS: more participants had normal scores for anxiety (65%) and depression (80%) at 6-months than at baseline (51 and 64%). More emergency therapy was prescribed during the study period compared to the previous year. Only 18 participants (39%) contacted the Light Touch Helpline during the 6-month study. Twenty patients provided a total of 36 interviews, 8 clinicians contributed to a focus group and 6 managers were interviewed. Patients considered that the oximetry readings heightened awareness of their condition and gave them confidence to make self-management decisions. Healthcare professionals valued oximetry as a tool for teaching people self-management skills, but were concerned that patients rarely contacted the teams for help or advice during the study.
Conclusions: 'Light Touch' shows promise as a low-cost strategy for empowering patients' self-management skills and reducing reliance on clinical supervision.
Figures

References
-
- Lozano R, Naghavi M, Foreman K, Lim S, Shibuya K, Aboyans V, et al. Global and regional mortality from 235 causes of death for 20 age groups in 1990 and 2010: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet. 2012;380:2095–128. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61728-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Liddell A, Adshead S, Burgess E. Technology in the NHS: transforming the patient’s experience of care. London: The King’s Fund; 2008.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

