Effect of Intermittent Hypoxia and Rimonabant on Glucose Metabolism in Rats: Involvement of Expression of GLUT4 in Skeletal Muscle
- PMID: 26503060
- PMCID: PMC4629628
- DOI: 10.12659/msm.896039
Effect of Intermittent Hypoxia and Rimonabant on Glucose Metabolism in Rats: Involvement of Expression of GLUT4 in Skeletal Muscle
Abstract
Background: Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and its main feature, chronic intermit-tent hypoxia (IH) during sleep, is closely associated with insulin resistance (IR) and diabetes. Rimonabant can regulate glucose metabolism and improve IR. The present study aimed to assess the effect of IH and rimonabant on glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity, and to explore the possible mechanisms.
Material and methods: Thirty-two rats were randomly assigned into 4 groups: Control group, subjected to intermittent air only; IH group, subjected to IH only; IH+NS group, subjected to IH and treated with normal saline; and IH+Rim group, subjected to IH and treated with 10 mg/kg/day of rimonabant. All rats were killed after 28 days of exposure. Then, the blood and skeletal muscle were collected. We measured fasting blood glucose levels, fasting blood insulin levels, and the expression of glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4) in both mRNA and protein levels in skeletal muscle.
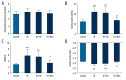
Results: IH can slow weight gain, increase serum insulin level, and reduce insulin sensitivity in rats. The expressions of GLUT4 mRNA, total GLUT4, and plasma membrane protein of GLUT4 (PM GLUT4) in skeletal muscle were decreased. Rimonabant treatment was demonstrated to improve weight gain and insulin sensitivity of the rats induced by IH. Rimonabant significantly upregulated the expression of GLUT4 mRNA, PM GLUT4, and total GLUT4 in skeletal muscle.
Conclusions: The present study demonstrates that IH can cause IR and reduced expression of GLUT4 in both mRNA and protein levels in skeletal muscle of rats. Rimonabant treatment can improve IH - induced IR, and the upregulation of GLUT4 expression may be involved in this process.
Figures




References
-
- Yang D, Liu Z, Yang H, Luo Q. Effects of continuous positive airway pressure on glycemic control and insulin resistance in patients with obstructive sleep apnea: a meta-analysis. Sleep Breath. 2013;17:33–38. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

