Retinal oxygen extraction in humans
- PMID: 26503332
- PMCID: PMC4621499
- DOI: 10.1038/srep15763
Retinal oxygen extraction in humans
Abstract
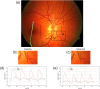
Adequate function of the retina is dependent on proper oxygen supply. In humans, the inner retina is oxygenated via the retinal circulation. We present a method to calculate total retinal oxygen extraction based on measurement of total retinal blood flow using dual-beam bidirectional Doppler optical coherence tomography and measurement of oxygen saturation by spectrophotometry. These measurements were done on 8 healthy subjects while breathing ambient room air and 100% oxygen. Total retinal blood flow was 44.3 ± 9.0 μl/min during baseline and decreased to 18.7 ± 4.2 μl/min during 100% oxygen breathing (P < 0.001) resulting in a pronounced decrease in retinal oxygen extraction from 2.33 ± 0.51 μl(O2)/min to 0.88 ± 0.14 μl(O2)/min during breathing of 100% oxygen. The method presented in this paper may have significant potential to study oxygen metabolism in hypoxic retinal diseases such as diabetic retinopathy.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

