Structural Dissection of the Maltodextrin Disproportionation Cycle of the Arabidopsis Plastidial Disproportionating Enzyme 1 (DPE1)
- PMID: 26504082
- PMCID: PMC4705983
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M115.682245
Structural Dissection of the Maltodextrin Disproportionation Cycle of the Arabidopsis Plastidial Disproportionating Enzyme 1 (DPE1)
Abstract
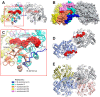
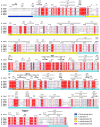
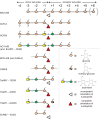
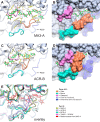
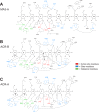
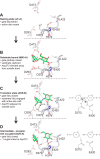
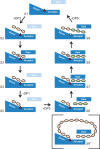
The degradation of transitory starch in the chloroplast to provide fuel for the plant during the night requires a suite of enzymes that generate a series of short chain linear glucans. However, glucans of less than four glucose units are no longer substrates for these enzymes, whereas export from the plastid is only possible in the form of either maltose or glucose. In order to make use of maltotriose, which would otherwise accumulate, disproportionating enzyme 1 (DPE1; a 4-α-glucanotransferase) converts two molecules of maltotriose to a molecule of maltopentaose, which can now be acted on by the degradative enzymes, and one molecule of glucose that can be exported. We have determined the structure of the Arabidopsis plastidial DPE1 (AtDPE1), and, through ligand soaking experiments, we have trapped the enzyme in a variety of conformational states. AtDPE1 forms a homodimer with a deep, long, and open-ended active site canyon contained within each subunit. The canyon is divided into donor and acceptor sites with the catalytic residues at their junction; a number of loops around the active site adopt different conformations dependent on the occupancy of these sites. The "gate" is the most dynamic loop and appears to play a role in substrate capture, in particular in the binding of the acceptor molecule. Subtle changes in the configuration of the active site residues may prevent undesirable reactions or abortive hydrolysis of the covalently bound enzyme-substrate intermediate. Together, these observations allow us to delineate the complete AtDPE1 disproportionation cycle in structural terms.
Keywords: Arabidopsis; acarbose; acarviostatin; carbohydrate metabolism; chloroplast; crystal structure; cycloamylose; disproportionating enzyme 1; glycosyltransferase; starch degradation.
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures




References
-
- Zeeman S. C., Kossmann J., and Smith A. M. (2010) Starch: its metabolism, evolution, and biotechnological modification in plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 61, 209–234 - PubMed
-
- Smith A. M. (2012) Starch in the Arabidopsis plant. Starch 64, 421–434
-
- Smirnova J., Fernie A. R., and Steup M. (2015) in Starch: Metabolism and Structure (Nakamura Y., ed) pp. 239–290, Springer Publishing, Tokyo
-
- Smith A. M., Zeeman S. C., and Smith S. M. (2005) Starch degradation. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 56, 73–98 - PubMed
-
- Delatte T., Umhang M., Trevisan M., Eicke S., Thorneycroft D., Smith S. M., and Zeeman S. C. (2006) Evidence for distinct mechanisms of starch granule breakdown in plants. J. Biol. Chem. 281, 12050–12059 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

