Differential ligand-signaling network of CCL19/CCL21-CCR7 system
- PMID: 26504105
- PMCID: PMC4620938
- DOI: 10.1093/database/bav106
Differential ligand-signaling network of CCL19/CCL21-CCR7 system
Abstract
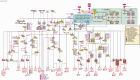
Chemokine (C-C motif) receptor 7 (CCR7), a class A subtype G-Protein Coupled Receptor (GPCR), is involved in the migration, activation and survival of multiple cell types including dendritic cells, T cells, eosinophils, B cells, endothelial cells and different cancer cells. Together, CCR7 signaling system has been implicated in diverse biological processes such as lymph node homeostasis, T cell activation, immune tolerance, inflammatory response and cancer metastasis. CCL19 and CCL21, the two well-characterized CCR7 ligands, have been established to be differential in their signaling through CCR7 in multiple cell types. Although the differential ligand signaling through single receptor have been suggested for many receptors including GPCRs, there exists no resource or platform to analyse them globally. Here, first of its kind, we present the cell-type-specific differential signaling network of CCL19/CCL21-CCR7 system for effective visualization and differential analysis of chemokine/GPCR signaling. Database URL: http:// www. netpath. org/ pathways? path_ id= NetPath_ 46.
© The Author(s) 2015. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Common and biased signaling pathways of the chemokine receptor CCR7 elicited by its ligands CCL19 and CCL21 in leukocytes.J Leukoc Biol. 2016 Jun;99(6):869-82. doi: 10.1189/jlb.2MR0815-380R. Epub 2016 Jan 4. J Leukoc Biol. 2016. PMID: 26729814 Review.
-
Biased Signaling of CCL21 and CCL19 Does Not Rely on N-Terminal Differences, but Markedly on the Chemokine Core Domains and Extracellular Loop 2 of CCR7.Front Immunol. 2019 Sep 13;10:2156. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02156. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31572374 Free PMC article.
-
Fluorescently Tagged CCL19 and CCL21 to Monitor CCR7 and ACKR4 Functions.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Dec 4;19(12):3876. doi: 10.3390/ijms19123876. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30518137 Free PMC article.
-
Arrestin 3 mediates endocytosis of CCR7 following ligation of CCL19 but not CCL21.J Immunol. 2008 Oct 1;181(7):4723-32. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.7.4723. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18802075 Free PMC article.
-
Biased signaling of G protein-coupled receptors - From a chemokine receptor CCR7 perspective.Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2018 Mar 1;258:4-14. doi: 10.1016/j.ygcen.2017.07.004. Epub 2017 Jul 8. Gen Comp Endocrinol. 2018. PMID: 28694053 Review.
Cited by
-
Latest update on chemokine receptors as therapeutic targets.Biochem Soc Trans. 2021 Jun 30;49(3):1385-1395. doi: 10.1042/BST20201114. Biochem Soc Trans. 2021. PMID: 34060588 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structural Insights into Molecular Recognition by Human Chemokine CCL19.Biochemistry. 2022 Mar 1;61(5):311-318. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.1c00759. Epub 2022 Feb 14. Biochemistry. 2022. PMID: 35156805 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic Landscape of Tumor-Infiltrating T and B Cells in Human Cancer.Front Immunol. 2022 Jan 4;12:731329. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.731329. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35069521 Free PMC article.
-
A brain proteomic signature of incipient Alzheimer's disease in young APOE ε4 carriers identifies novel drug targets.Sci Adv. 2021 Nov 12;7(46):eabi8178. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abi8178. Epub 2021 Nov 10. Sci Adv. 2021. PMID: 34757788 Free PMC article.
-
Interplay between CCR7 and Notch1 axes promotes stemness in MMTV-PyMT mammary cancer cells.Mol Cancer. 2017 Jan 31;16(1):19. doi: 10.1186/s12943-017-0592-0. Mol Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28137279 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cyster J.G. (1999) Chemokines and cell migration in secondary lymphoid organs. Science, 286, 2098–2102. - PubMed
-
- Yasuda T., Kuwabara T., Nakano H., et al. (2007) Chemokines CCL19 and CCL21 promote activation-induced cell death of antigen-responding T cells. Blood, 109, 449–456. - PubMed
-
- Halvorsen B., Dahl T.B., Smedbakken L.M., et al. (2014) Increased levels of CCR7 ligands in carotid atherosclerosis: different effects in macrophages and smooth muscle cells. Cardiovasc. Res., 102, 148–156. - PubMed
-
- Damås J.K., Smith C., Øie E., et al. (2007) Enhanced expression of the homeostatic chemokines CCL19 and CCL21 in clinical and experimental atherosclerosis: possible pathogenic role in plaque destabilization. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol.,27, 614–620. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

