Enzymes: principles and biotechnological applications
- PMID: 26504249
- PMCID: PMC4692135
- DOI: 10.1042/bse0590001
Enzymes: principles and biotechnological applications
Erratum in
- Essays Biochem. 2015;59:75
Abstract
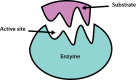
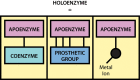
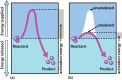
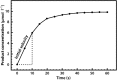
Enzymes are biological catalysts (also known as biocatalysts) that speed up biochemical reactions in living organisms, and which can be extracted from cells and then used to catalyse a wide range of commercially important processes. This chapter covers the basic principles of enzymology, such as classification, structure, kinetics and inhibition, and also provides an overview of industrial applications. In addition, techniques for the purification of enzymes are discussed.
© 2015 Authors.
Figures
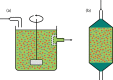

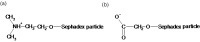

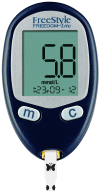
Similar articles
-
Extreme Biocatalysts: From Basic Research to Biotechnological Applications.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 12;25(12):6492. doi: 10.3390/ijms25126492. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38928198 Free PMC article.
-
A roadmap to directed enzyme evolution and screening systems for biotechnological applications.Biol Res. 2013;46(4):395-405. doi: 10.4067/S0716-97602013000400011. Biol Res. 2013. PMID: 24510142 Review.
-
Biotechnological applications of archaeal enzymes from extreme environments.Biol Res. 2018 Oct 5;51(1):37. doi: 10.1186/s40659-018-0186-3. Biol Res. 2018. PMID: 30290805 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Utilization of enzymes for environmental applications.Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2004;24(2-3):125-54. doi: 10.1080/07388550490493726. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2004. PMID: 15493529 Review.
-
Exploiting the versatility and selectivity of Mo enzymes with electrochemistry.Chem Commun (Camb). 2011 Feb 14;47(6):1663-73. doi: 10.1039/c0cc03681a. Epub 2010 Dec 24. Chem Commun (Camb). 2011. PMID: 21186382
Cited by
-
Recent advancements in enzyme-mediated crosslinkable hydrogels: In vivo-mimicking strategies.APL Bioeng. 2021 Apr 1;5(2):021502. doi: 10.1063/5.0037793. eCollection 2021 Jun. APL Bioeng. 2021. PMID: 33834154 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Presence of small resistant peptides from new in vitro digestion assays detected by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry: An implication of allergenicity prediction of novel proteins?PLoS One. 2020 Jun 15;15(6):e0233745. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0233745. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32542029 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in Lipid Metabolites and Enzyme Activities of Wheat Flour during Maturation.Foods. 2024 Aug 14;13(16):2537. doi: 10.3390/foods13162537. Foods. 2024. PMID: 39200465 Free PMC article.
-
Evidential deep learning for trustworthy prediction of enzyme commission number.Brief Bioinform. 2023 Nov 22;25(1):bbad401. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbad401. Brief Bioinform. 2023. PMID: 37991247 Free PMC article.
-
An Oligopeptide-Protected Ultrasmall Gold Nanocluster with Peroxidase-Mimicking and Cellular-Imaging Capacities.Molecules. 2022 Dec 21;28(1):70. doi: 10.3390/molecules28010070. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36615266 Free PMC article.
References
Recommended reading and key publications
1. Historically important landmark papers (in chronological order)
-
- Takamine J. Process of making diastatic enzyme. 1894 U.S. Pat. 525,823. Describes the first commercial exploitation of semi-purified enzymes in the West.
-
- Clark L.C., Jr, Lyons C. Electrode systems for continuous monitoring in cardiovascular surgery. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 1962;102:29–45. Introduces the concept of a biosensor for measuring blood glucose levels during surgery. - PubMed
-
- Monod J., Wyman H., Changeux J.P. On the nature of allosteric transitions: a plausible model. J. Mol. Biol. 1965;12:88–118. Describes the ‘concerted’ model of transitions of allosteric proteins in which all constituent monomers are in either the T-state or the R-state. - PubMed
2. Enzyme principles
-
- Changeux J.-P. 50 years of allosteric interactions: the twists and turns of the models. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013;14:819–829. - PubMed
-
- Kamata K., Mitsuya M., Nishimura T., Eiki J., Nagata Y. Structural basis for allosteric regulation of the monomeric allosteric enzyme human glucokinase. Structure. 2004;12:429–438. - PubMed
3. Enzyme applications
-
- Clarke S.F., Foster J.R. A history of blood glucose meters and their role in self-monitoring of diabetes mellitus. Br. J. Biomed. Sci. 2012;69:83–93. - PubMed
-
- Vashist S.K., Zheng D., Al-Rubeaan K., Luong J.H.T., Sheu F.-S. Technology behind commercial devices for blood glucose monitoring in diabetes management: a review. Anal. Chim. Acta. 2011;703:124–136. - PubMed
-
- Vellard M. The enzyme as drug: application of enzymes as pharmaceuticals. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2003;14:444–450. - PubMed
4. Useful textbooks
-
- Bisswanger H. Enzyme Kinetics: Principles and Methods. 2nd edn. Weinheim, Germany: Wiley-VCH; 2008. Available online and as hard copy. A user-friendly and comprehensive treatise on enzyme kinetics.
-
- Buchholz K., Kasche V., Bornscheuer U.T. Biocatalysts and Enzyme Technology. 2nd edn. Weinheim, Germany: Wiley-VCH; 2012. Best-selling textbook that provides an instructive and comprehensive overview of our current knowledge of biocatalysis and enzyme technology.
-
- Copeland R.A. In: Evaluation of Enzyme Inhibitors in Drug Discovery: A Guide for Medicinal Chemists and Pharmacologists. 2nd edn. Hoboken NJ., editor. John Wiley & Sons, Inc; 2013. Provides thorough coverage of both the principles and applications of enzyme inhibitors. - PubMed
-
- McGrath M.J., Scanaill C.N. Sensor Technologies: Healthcare, Wellness and Environmental Applications. New York: Apress Media, LLC; 2014. Available online. Covers sensor technologies and their clinical applications, together with broader applications that are relevant to wellness, fitness, lifestyle and the environment.
-
- Trevan M.D. Immobilized Enzymes: An Introduction and Applications in Biotechnology. Chichester: John Wiley & Sons; 1980. An older text, and difficult to find except in libraries, but it provides an introductory text for non-experts, and as yet there is no other book that fulfils this role.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

