Cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen (CMRO2) assessed by combined Doppler and spectroscopic OCT
- PMID: 26504644
- PMCID: PMC4605053
- DOI: 10.1364/BOE.6.003941
Cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen (CMRO2) assessed by combined Doppler and spectroscopic OCT
Abstract
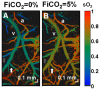
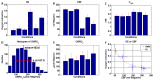
A method of measuring cortical oxygen metabolism in the mouse brain that uses independent quantitative measurements of three key parameters: cerebral blood flow (CBF), arteriovenous oxygen extraction (OE), and hemoglobin concentration ([HbT]) is presented. Measurements were performed using a single visible light spectral/Fourier domain OCT microscope, with Doppler and spectroscopic capabilities, through a thinned-skull cranial window in the mouse brain. Baseline metabolic measurements in mice are shown to be consistent with literature values. Oxygen consumption, as measured by this method, did not change substantially during minor changes either in the fraction of inspired oxygen (FiO2) or in the fraction of inspired carbon dioxide (FiCO2), in spite of larger variations in oxygen saturations. This set of experiments supports, but does not prove, the validity of the proposed method of measuring brain oxygen metabolism.
Keywords: (110.4500) Optical coherence tomography; (170.0180) Microscopy; (170.1470) Blood or tissue constituent monitoring; (170.3880) Medical and biological imaging; (170.5380) Physiology.
Figures



References
-
- Østergaard L., Engedal T. S., Aamand R., Mikkelsen R., Iversen N. K., Anzabi M., Næss-Schmidt E. T., Drasbek K. R., Bay V., Blicher J. U., Tietze A., Mikkelsen I. K., Hansen B., Jespersen S. N., Juul N., Sørensen J. C., Rasmussen M., “Capillary transit time heterogeneity and flow-metabolism coupling after traumatic brain injury,” J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 34(10), 1585–1598 (2014).10.1038/jcbfm.2014.131 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
