A modified false vocal fold flap for functional reconstruction after frontolateral partial laryngectomy: a comparison with conventional open resection and laser cordectomy
- PMID: 26504705
- PMCID: PMC4582486
- DOI: 10.3205/iprs000034
A modified false vocal fold flap for functional reconstruction after frontolateral partial laryngectomy: a comparison with conventional open resection and laser cordectomy
Abstract
Objective: To describe a modified flap technique (MFT) involving the use of a false vocal fold flap for glottic reconstruction and the removal of arytenoid cartilage and to compare it with conventional frontolateral partial laryngectomy (FLPL) and laser cordectomy (LC).
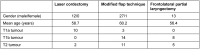
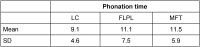
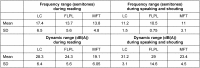
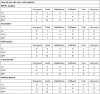
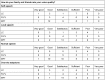
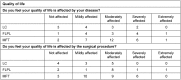
Methods: Twenty-eight MFT, 13 FLPL and 12 LC patients completed a standardised questionnaire for assessing aspiration, respiration, quality of life, and subjective voice quality. We analysed vocal function in terms of roughness, breathiness and hoarseness, measured voice range profiles, and performed videoendoscopy.
Results: No patient reported respiratory problems. Aspiration occurred in 33.3% (MFT), 41.6% (FLPL) and 16.6% (LC). Voice quality was rated as good/satisfactory by 17 MFT patients (62%), satisfactory/sufficient by 69% of FLKT patients, and sufficient/poor by 75% of LC patients.
Conclusions: The modified false vocal fold flap effectively covers defects and creates a neocord that ensures good phonatory rehabilitation and has positive effects on postoperative quality of life.
Hintergrund: Vergleich einer neuen Technik zur Rekonstruktion der Neoglottis mit Aryknorpel-Resektion (mTBP) im Vergleich zur konventionellen Teilresektion (FLKT) und Laserchordektomie.Material/Methoden: 28 Patienten (mTBP), 13 Patienten (FLKT) und 12 Patienten (Laser) wurden mittels eines standardisierten Fragebogens zu Aspirationsproblematik, Atmungsbeschwerden, peri- und postoperativer Lebensqualität sowie subjektiver Stimmqualität befragt. Ferner erfolgten eine Analyse der Stimmfunktion nach dem RBH-Schema, eine Stimmfelduntersuchung und eine Videoendoskopie.Ergebnisse: Keine Beschwerden bezüglich der Atmung. Hinsichtlich der Atmung wurden in keiner Gruppe postoperative Beschwerden angegeben. Aspiration bei 33,3% (mTBP), 41,6% (FLKT), 16,6% (Laser). Stimmqualität: mTBP 17 Patienten (62%) gut bis befriedigend, FLKT 69% befriedigend bis ausreichend, Laser 75% ausreichend bis schlecht.Schlussfolgerung: Die erweiterte Taschenbandplastik zur Glottisrekonstruktion nach frontolateraler Kehlkopfteilresektion ermöglicht neben einer guten Defektdeckung, die Ausbildung eines suffizienten Ersatzstimmbandes mit einer guten phonatorischen Rehabilitation, die sich auch positiv auf die postoperative Lebensqualität auswirkt.
Keywords: laser cordectomy; partial laryngectomy; quality of life; voice quality.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Vocal function after vertical partial laryngectomy with glottic reconstruction by false vocal fold flap: durational and frequency measures.Laryngoscope. 1999 May;109(5):698-704. doi: 10.1097/00005537-199905000-00004. Laryngoscope. 1999. PMID: 10334216 Clinical Trial.
-
Phonatory mechanisms after vertical partial laryngectomy with glottic reconstruction by false vocal fold flap.Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2001 Oct;110(10):935-40. doi: 10.1177/000348940111001008. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2001. PMID: 11642426 Clinical Trial.
-
[Estimation of quality of voice after removal of neoplasms T1 and T2 of glottis with simultaneous reconstruction of vocal fold with pedunculated sterno-thyroid muscle flap].Otolaryngol Pol. 2014 Sep-Oct;68(5):258-63. doi: 10.1016/j.otpol.2014.04.001. Epub 2014 Apr 18. Otolaryngol Pol. 2014. PMID: 25283323 Polish.
-
[CO2 laser cordectomy: analysis of morpho-functional results].Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2000 Apr;20(2):106-20. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2000. PMID: 10992603 Italian.
-
Laser microsurgical bilateral posterior cordectomy for the treatment of bilateral vocal fold paralysis.Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2005 Aug;114(8):599-604. doi: 10.1177/000348940511400804. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2005. PMID: 16190092
Cited by
-
Viscoelastic properties of human aryepiglottic fold and ventricular fold tissues at phonatory frequencies.Laryngoscope. 2018 Aug;128(8):E296-E301. doi: 10.1002/lary.27049. Epub 2017 Dec 15. Laryngoscope. 2018. PMID: 29243255 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Remacle M. Treatment with laser CO2 cordectomy and clinical implications in management of mild and moderate laryngeal precancerosis. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2008 Feb;265(2):261–262. doi: 10.1007/s00405-007-0481-z. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00405-007-0481-z. - DOI - DOI - PubMed
-
- Remacle M, Van Haverbeke C, Eckel H, Bradley P, Chevalier D, Djukic V, de Vicentiis M, Friedrich G, Olofsson J, Peretti G, Quer M, Werner J. Proposal for revision of the European Laryngological Society classification of endoscopic cordectomies. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2007 May;264(5):499–504. doi: 10.1007/s00405-007-0279-z. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00405-007-0279-z. - DOI - DOI - PubMed
-
- Peretti G, Piazza C, Cattaneo A, De Benedetto L, Martin E, Nicolai P. Comparison of functional outcomes after endoscopic versus open-neck supraglottic laryngectomies. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol. 2006 Nov;115(11):827–832. - PubMed
-
- Schröder U, Schönweiler R, Wollenberg B, Gehrking E. Einseitige erweiterte Medialisierungs-Thyroplastik. Therapie der kompletten Aspiration nach laserchirurgischer Resektion und Strahlentherapie des Larynxkarzinoms. [Unilateral extended medialization thyroplasty. Treatment for total aspiration after laser surgery and radiotherapy of laryngeal cancer]. HNO. 2008 Apr;56(4):467–470. doi: 10.1007/s00106-008-1704-3. (Ger). Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00106-008-1704-3. - DOI - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sittel C, Plinkert PK. Stimmlippenaugmentation. [Vocal fold augmentation]. HNO. 2005 Jan;53(1):6–10. doi: 10.1007/s00106-004-1196-8. (Ger). Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00106-004-1196-8. - DOI - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

