External transpedicular spine fixation in severe spondylodiscitis - salvage procedure
- PMID: 26504709
- PMCID: PMC4582483
- DOI: 10.3205/iprs000038
External transpedicular spine fixation in severe spondylodiscitis - salvage procedure
Abstract
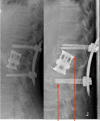
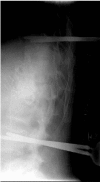
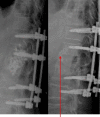
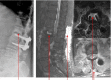
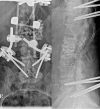
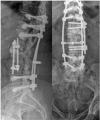
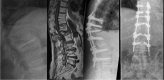
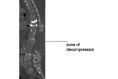
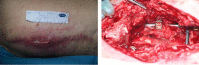
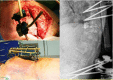
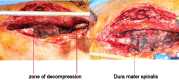
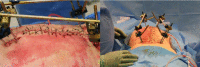
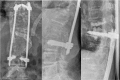
Specific and non-specific infections of the spine are rare. Due to their potential for severe instabilities, deformities and the impairment of neurological structures, the treatment is often prolonged and needs an interdisciplinary management. The clinical presentation is uncharacteristic, therefore diagnosis is often delayed. There are no prospective randomized studies for therapy recommendation. The surgical concept includes eradication of the infection and the reliable stabilization of involved segments. This concept is successful in most cases of endogenous vertebral osteomyelitis. The therapy of the exogenous spine infections after macro and micro surgery is more difficult, due to the critical wound situation and the involvement of the posterior parts of the spine. In these cases, infection-associated instability of the anterior part is complicated by critical posterior wound conditions. We present three cases of severe exogenous vertebral infections, where temporary external transpedicular spine fixation was used for salvage procedure, till soft tissue conditions have permitted a definitive internal stabilization.
Spezifische und unspezifische Infektionen der Wirbelsäule sind selten. Aufgrund ihres Potentials für hochgradige Instabilitäten, Deformitäten und der Beeinträchtigung neurologischer Strukturen ist die Behandlung oft prolongiert und erfordert ein interdisziplinäres Management. Die klinische Symptomatik ist uncharakteristisch, daher wird die Diagnose oft verzögert gestellt. Es gibt keine prospektiv randomisierten Studien zur Therapieempfehlung. Das operative Konzept umfasst die chirurgische Infekteradikation und die sichere Stabilisierung der involvierten Segmente. Dieses Vorgehen ist in den meisten Fällen der endogenen Wirbelkörperosteomyelitis erfolgreich. Die Therapie der exogenen Spondylodiszitis nach Makro- und mirkochirurgischen Eingriffen ist aufgrund der kritischen Wundverhältnisse und der Beteiligung der dorsalen Abschnitte der Wirbelsäule weitaus schwieriger. In diesen Fällen wird die infekt-bedingte Instabilität der vorderen Säule durch die infizierten dorsalen Weichteilverhältnisse kompliziert. Wir präsentieren drei Fälle schwerer exogener Spondylodiszitiden, in denen die temporäre Stabilisierung durch Fixateur externe als Salvage-Verfahren genutzt wurde, bis die lokalen Weichteilverhältnisse eine definitive interne Stabilisierung zugelassen haben.
Keywords: exogenous spine infection; exogenous vertebral osteomyelitis; external spine fixation; spondylodiscitis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Sequential or simultaneous, same-day anterior decompression and posterior stabilization in the management of vertebral osteomyelitis of the lumbar spine.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1998 Sep 1;23(17):1885-90. doi: 10.1097/00007632-199809010-00018. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1998. PMID: 9762746
-
Treatment of osteomyelitis of the spine using percutaneous suction/irrigation and percutaneous external spinal fixation.J Spinal Disord. 1994 Jun;7(3):185-205. doi: 10.1097/00002517-199407030-00001. J Spinal Disord. 1994. PMID: 7919642 Review.
-
Posterior fixation without debridement for vertebral body osteomyelitis and discitis.Neurosurg Focus. 2014 Aug;37(2):E6. doi: 10.3171/2014.6.FOCUS14142. Neurosurg Focus. 2014. PMID: 25081966
-
External fixation of the spine: surgical salvage option for complex spinal infections.Surg Technol Int. 2010 Apr;19:223-8. Surg Technol Int. 2010. PMID: 20437368
-
Clinical features, diagnostic and therapeutic approaches to haematogenous vertebral osteomyelitis.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2005 Jan-Feb;9(1):53-66. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2005. PMID: 15852519 Review.
References
-
- Acosta FL, Jr, Chin CT, Quiñones-Hinojosa A, Ames CP, Weinstein PR, Chou D. Diagnosis and management of adult pyogenic osteomyelitis of the cervical spine. Neurosurg Focus. 2004 Dec;17(6):E2. doi: 10.3171/foc.2004.17.6.2. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.3171/foc.2004.17.6.2. - DOI - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bednar DA. Failure of external spinal skeletal fixation to improve predictability of lumbar arthrodesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2001 Nov;83-A(11):1656–1659. - PubMed
-
- Carragee EJ. Pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1997 Jun;79(6):874–880. - PubMed
-
- Carragee EJ. The clinical use of magnetic resonance imaging in pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis. Spine. 1997 Apr;22(7):780–785. doi: 10.1097/00007632-199704010-00015. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1097/00007632-199704010-00015. - DOI - DOI - PubMed
-
- Cramer J, Haase N, Behre I, Ostermann PAW. Spondylitis und Spondylodiszitis. Trauma und Berufskrankheit. 2003;5:336–41. doi: 10.1007/s10039-003-0771-7. Available from: http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s10039-003-0771-7. - DOI - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

