On the impact of epidemic severity on network immunization algorithms
- PMID: 26505554
- PMCID: PMC7126281
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tpb.2015.10.007
On the impact of epidemic severity on network immunization algorithms
Abstract
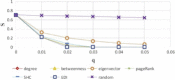
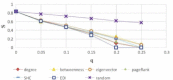
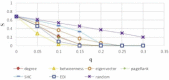
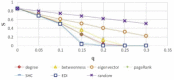
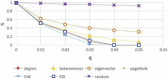
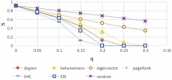
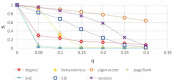
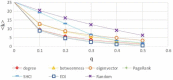
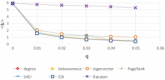
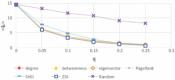
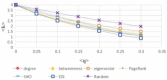
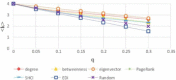
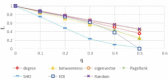
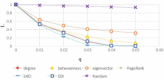
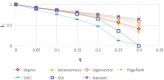
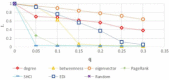
There has been much recent interest in the prevention and mitigation of epidemics spreading through contact networks of host populations. Here, we investigate how the severity of epidemics, measured by its infection rate, influences the efficiency of well-known vaccination strategies. In order to assess the impact of severity, we simulate the SIR model at different infection rates on various real and model immunized networks. An extensive analysis of our simulation results reveals that immunization algorithms, which efficiently reduce the nodes' average degree, are more effective in the mitigation of weak and slow epidemics, whereas vaccination strategies that fragment networks to small components, are more successful in suppressing severe epidemics.
Keywords: Complex networks; Epidemic model; Graph; Immunization algorithms; Infection rate.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures














Similar articles
-
Suppression of epidemic spreading process on multiplex networks via active immunization.Chaos. 2019 Jul;29(7):073111. doi: 10.1063/1.5093047. Chaos. 2019. PMID: 31370413
-
The impact of vaccine failure rate on epidemic dynamics in responsive networks.Chaos. 2015 Apr;25(4):043116. doi: 10.1063/1.4919245. Chaos. 2015. PMID: 25933664
-
The impact of media converge on complex networks on disease transmission.Math Biosci Eng. 2019 Jul 9;16(6):6335-6349. doi: 10.3934/mbe.2019316. Math Biosci Eng. 2019. PMID: 31698565
-
Understanding infectious agents from an in silico perspective.Drug Discov Today. 2011 Jan;16(1-2):42-9. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2010.10.007. Epub 2010 Oct 23. Drug Discov Today. 2011. PMID: 20974283 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Concepts in Understanding Infectious Disease Dynamics in Populations.Vet Clin North Am Food Anim Pract. 2025 Mar;41(1):1-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cvfa.2024.11.001. Epub 2025 Jan 2. Vet Clin North Am Food Anim Pract. 2025. PMID: 39746828 Review.
Cited by
-
On the effectiveness of random walks for modeling epidemics on networks.PLoS One. 2023 Jan 10;18(1):e0280277. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0280277. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 36626406 Free PMC article.
-
Mathematical epidemiology for a later age.Theor Popul Biol. 2022 Apr;144:81-83. doi: 10.1016/j.tpb.2022.02.004. Epub 2022 Mar 2. Theor Popul Biol. 2022. PMID: 35247319 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Optimizing targeted vaccination across cyber-physical networks: an empirically based mathematical simulation study.J R Soc Interface. 2018 Jan;15(138):20170783. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2017.0783. J R Soc Interface. 2018. PMID: 29298957 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bonacich P. Power and centrality: A family of measures. Am. J. Sociol. 1987;92:1170–1182.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

