Molecular heterogeneity of midbrain dopaminergic neurons--Moving toward single cell resolution
- PMID: 26505674
- PMCID: PMC4679573
- DOI: 10.1016/j.febslet.2015.10.022
Molecular heterogeneity of midbrain dopaminergic neurons--Moving toward single cell resolution
Abstract
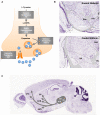
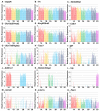
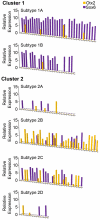
Since their discovery, midbrain dopamine (DA) neurons have been researched extensively, in part because of their diverse functions and involvement in various neuropsychiatric disorders. Over the last few decades, reports have emerged that midbrain DA neurons were not a homogeneous group, but that DA neurons located in distinct anatomical locations within the midbrain had distinctive properties in terms of physiology, function, and vulnerability. Accordingly, several studies focused on identifying heterogeneous gene expression across DA neuron clusters. Here we review the importance of understanding DA neuron heterogeneity at the molecular level, previous studies detailing heterogeneous gene expression in DA neurons, and finally recent work which brings together previous heterogeneous gene expression profiles in a coordinated manner, at single cell resolution.
Keywords: Dopamine neuron subtypes; Midbrain; Molecular diversity; Selective vulnerability; Single cell expression profiling.
Copyright © 2015 Federation of European Biochemical Societies. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Dahlstroem A, Fuxe K. Evidence for the Existence of Monoamine-Containing Neurons in the Central Nervous System. I. Demonstration of Monoamines in the Cell Bodies of Brain Stem Neurons. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1964;(SUPPL 232):231–255. - PubMed
-
- Carlsson A, Falck B, Hillarp NA. Cellular localization of brain monoamines. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1962;56:1–28. - PubMed
-
- Ehringer H, Hornykiewicz O. [Distribution of noradrenaline and dopamine (3-hydroxytyramine) in the human brain and their behavior in diseases of the extrapyramidal system] Klinische Wochenschrift. 1960;38:1236–1239. - PubMed
-
- Bjorklund A, Dunnett SB. Fifty years of dopamine research. Trends Neurosci. 2007;30:185–187. - PubMed
-
- Bjorklund A, Dunnett SB. Dopamine neuron systems in the brain: an update. Trends Neurosci. 2007;30:194–202. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

