Biosorption of Cadmium and Manganese Using Free Cells of Klebsiella sp. Isolated from Waste Water
- PMID: 26505890
- PMCID: PMC4623521
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0140962
Biosorption of Cadmium and Manganese Using Free Cells of Klebsiella sp. Isolated from Waste Water
Erratum in
-
Correction: Biosorption of Cadmium and Manganese Using Free Cells of Klebsiella sp. Isolated from Waste Water.PLoS One. 2018 May 24;13(5):e0198309. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0198309. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29795699 Free PMC article.
Abstract
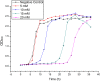
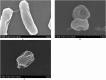
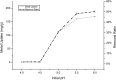
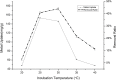
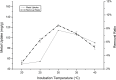
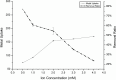
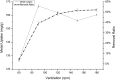
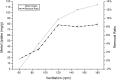
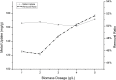
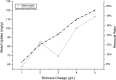
In the present study, we evaluated a bacterium that was isolated from waste water for its ability to take up cadmium and manganese. The strain, identified both biochemically and by its 16S rRNA gene sequence as Klebsiella, was named Yangling I2 and was found to be highly resistant to heavy metals. Surface characterization of the bacterium via SEM revealed gross morphological changes, with cells appearing as biconcave discs after metal exposure rather than their typical rod shape. The effects of pH, temperature, heavy metal concentration, agitation and biomass concentration on the uptake of Cd(II) and Mn(II) was measured using atomic absorption spectrophotometry. The results showed that the biosorption was most affected by pH and incubation temperature, being maximized at pH 5.0 and 30°C, with absorption capacities of 170.4 and 114.1 mg/g for Cd(II) and Mn(II), respectively. Two models were investigated to compare the cells' capacity for the biosorption of Cd and Mn, and the Langmuir model based on fuzzy linear regression was found to be close to the observed absorption curves and yield binding constants of 0.98 and 0.86 for Cd and Mn, respectively. This strain of Klebsiella has approximately ten times the absorption capacity reported for other strains and is promising for the removal of heavy metals from waste water.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures





Similar articles
-
Characterization of Cd2+ biosorption by Pseudomonas sp. strain 375, a novel biosorbent isolated from soil polluted with heavy metals in Southern China.Chemosphere. 2020 Feb;240:124893. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124893. Epub 2019 Sep 17. Chemosphere. 2020. PMID: 31550585
-
Potential application of Staphylococcus devriesei MS as a biosorbent agent for manganase, chromium, and cadmium heavy metals in contaminated water.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 21;15(1):9774. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-91961-6. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40118989 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of biosorption potential of Brevibacillus biomass isolated from contaminated water resources for removal of Pb (II) ions.Water Sci Technol. 2022 Apr;85(8):2358-2374. doi: 10.2166/wst.2022.110. Water Sci Technol. 2022. PMID: 35486460
-
Improvement of Zn (II) and Cd (II) Biosorption by Priestia megaterium PRJNA526404 Isolated from Agricultural Waste Water.Microorganisms. 2022 Dec 19;10(12):2510. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10122510. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 36557763 Free PMC article.
-
Perinatal and Childhood Exposure to Cadmium, Manganese, and Metal Mixtures and Effects on Cognition and Behavior: A Review of Recent Literature.Curr Environ Health Rep. 2015 Sep;2(3):284-94. doi: 10.1007/s40572-015-0058-8. Curr Environ Health Rep. 2015. PMID: 26231505 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Correction: Biosorption of Cadmium and Manganese Using Free Cells of Klebsiella sp. Isolated from Waste Water.PLoS One. 2018 May 24;13(5):e0198309. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0198309. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29795699 Free PMC article.
-
Alleviating arsenic stress affecting the growth of Vigna radiata through the application of Klebsiella strain ASBT-KP1 isolated from wastewater.Front Microbiol. 2024 Sep 25;15:1484069. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1484069. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39386362 Free PMC article.
-
Cadmium Removal from Aqueous Solutions by Strain of Pantoea agglomerans UCP1320 Isolated from Laundry Effluent.Open Microbiol J. 2018 Aug 31;12:297-307. doi: 10.2174/1874285801812010297. eCollection 2018. Open Microbiol J. 2018. PMID: 30288185 Free PMC article.
-
Isotherm and kinetic studies of cadmium biosorption and its adsorption behaviour in multi-metals solution using dead and immobilized archaeal cells.Sci Rep. 2023 Feb 13;13(1):2550. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-29456-5. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36781949 Free PMC article.
-
Cd-Resistant Strains of B. cereus S5 with Endurance Capacity and Their Capacities for Cadmium Removal from Cadmium-Polluted Water.PLoS One. 2016 Apr 14;11(4):e0151479. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0151479. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27077388 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wang JL, Chen C (2006) Biosorption of heavy metals by Saccharomyces cerevisiae: A review. Biotechnology Advances 24: 427–451. - PubMed
-
- Buxbaum G (2008) Industrial inorganic pigments: John Wiley & Sons.
-
- Scoullos M (2001) Mercury, cadmium, lead: Handbook for sustainable heavy metals policy and regulation: Springer.
-
- Benguella B, Benaissa H (2002) Cadmium removal from aqueous solutions by chitin: kinetic and equilibrium studies. Water Research 36: 2463–2474. - PubMed
-
- Yin J, Blanch HW (1989) A bio-mimetic cadmium adsorbent: Design, synthesis, and characterization. Biotechnology and Bioengineering 34: 180–188. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

