Molecular profiling of low grade serous ovarian tumours identifies novel candidate driver genes
- PMID: 26506417
- PMCID: PMC4741956
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.5438
Molecular profiling of low grade serous ovarian tumours identifies novel candidate driver genes
Abstract
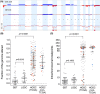
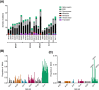
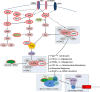
Low grade serous ovarian tumours are a rare and under-characterised histological subtype of epithelial ovarian tumours, with little known of the molecular drivers and facilitators of tumorigenesis beyond classic oncogenic RAS/RAF mutations. With a move towards targeted therapies due to the chemoresistant nature of this subtype, it is pertinent to more fully characterise the genetic events driving this tumour type, some of which may influence response to therapy and/or development of drug resistance. We performed genome-wide high-resolution genomic copy number analysis (Affymetrix SNP6.0) and mutation hotspot screening (KRAS, BRAF, NRAS, HRAS, ERBB2 and TP53) to compare a large cohort of ovarian serous borderline tumours (SBTs, n = 57) with low grade serous carcinomas (LGSCs, n = 19). Whole exome sequencing was performed for 13 SBTs, nine LGSCs and one mixed low/high grade carcinoma. Copy number aberrations were detected in 61% (35/57) of SBTs, compared to 100% (19/19) of LGSCs. Oncogenic RAS/RAF/ERBB2 mutations were detected in 82.5% (47/57) of SBTs compared to 63% (12/19) of LGSCs, with NRAS mutations detected only in LGSC. Some copy number aberrations appeared to be enriched in LGSC, most significantly loss of 9p and homozygous deletions of the CDKN2A/2B locus. Exome sequencing identified BRAF, KRAS, NRAS, USP9X and EIF1AX as the most frequently mutated genes. We have identified markers of progression from borderline to LGSC and novel drivers of LGSC. USP9X and EIF1AX have both been linked to regulation of mTOR, suggesting that mTOR inhibitors may be a key companion treatment for targeted therapy trials of MEK and RAF inhibitors.
Keywords: borderline; copy number; exome; genomics; serous ovarian tumor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Schmeler KM, Gershenson DM. Low-grade serous ovarian cancer: a unique disease. Curr Oncol Rep. 2008;10:519–523. - PubMed
-
- Ali RH, Kalloger SE, Santos JL, Swenerton KD, Gilks CB. Stage II to IV low-grade serous carcinoma of the ovary is associated with a poor prognosis: a clinicopathologic study of 32 patients from a population-based tumor registry. Int J Gynecol Pathol. 2013;32:529–535. - PubMed
-
- Silva EG, Gershenson DM, Malpica A, Deavers M. The recurrence and the overall survival rates of ovarian serous borderline neoplasms with noninvasive implants is time dependent. Am J Surg Pathol. 2006;30:1367–1371. - PubMed
-
- Longacre TA, McKenney JK, Tazelaar HD, Kempson RL, Hendrickson MR. Ovarian serous tumors of low malignant potential (borderline tumors): outcome-based study of 276 patients with long-term (> or = 5-year) follow-up. Am J Surg Pathol. 2005;29:707–723. - PubMed
-
- Anglesio MS, Arnold JM, George J, Tinker AV, Tothill R, Waddell N, Simms L, Locandro B, Fereday S, Traficante N, Russell P, Sharma R, Birrer MJ, deFazio A, Chenevix-Trench G, Bowtell DD. Mutation of ERBB2 provides a novel alternative mechanism for the ubiquitous activation of RAS-MAPK in ovarian serous low malignant potential tumors. Mol Cancer Res. 2008;6:1678–1690. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

