Mandibulofacial Dysostosis with Microcephaly: Mutation and Database Update
- PMID: 26507355
- PMCID: PMC5512564
- DOI: 10.1002/humu.22924
Mandibulofacial Dysostosis with Microcephaly: Mutation and Database Update
Abstract
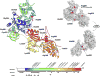
Mandibulofacial dysostosis with microcephaly (MFDM) is a multiple malformation syndrome comprising microcephaly, craniofacial anomalies, hearing loss, dysmorphic features, and, in some cases, esophageal atresia. Haploinsufficiency of a spliceosomal GTPase, U5-116 kDa/EFTUD2, is responsible. Here, we review the molecular basis of MFDM in the 69 individuals described to date, and report mutations in 38 new individuals, bringing the total number of reported individuals to 107 individuals from 94 kindreds. Pathogenic EFTUD2 variants comprise 76 distinct mutations and seven microdeletions. Among point mutations, missense substitutions are infrequent (14 out of 76; 18%) relative to stop-gain (29 out of 76; 38%), and splicing (33 out of 76; 43%) mutations. Where known, mutation origin was de novo in 48 out of 64 individuals (75%), dominantly inherited in 12 out of 64 (19%), and due to proven germline mosaicism in four out of 64 (6%). Highly penetrant clinical features include, microcephaly, first and second arch craniofacial malformations, and hearing loss; esophageal atresia is present in an estimated ∼27%. Microcephaly is virtually universal in childhood, with some adults exhibiting late "catch-up" growth and normocephaly at maturity. Occasionally reported anomalies, include vestibular and ossicular malformations, reduced mouth opening, atrophy of cerebral white matter, structural brain malformations, and epibulbar dermoid. All reported EFTUD2 mutations can be found in the EFTUD2 mutation database (http://databases.lovd.nl/shared/genes/EFTUD2).
Keywords: EFTUD2; MFDM; mandibulofacial dysostosis; mandibulofacial dysostosis Guion-Almeida type; mandibulofacial dysostosis with microcephaly; microcephaly.
© 2015 WILEY PERIODICALS, INC.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Bernier FP, Caluseriu O, Ng S, Schwartzentruber J, Buckingham KJ, Innes AM, Jabs EW, Innis JW, Schuette JL, Gorski JL, Byers PH, Andelfinger G, et al. Haploinsufficiency of SF3B4, a component of the pre-mRNA spliceosomal complex, causes Nager syndrome. Am J Hum Genet. 2012;90:925–933. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dauwerse JG, Dixon J, Seland S, Ruivenkamp CA, van Haeringen A, Hoefsloot LH, Peters DJ, Boers AC, Daumer-Haas C, Maiwald R, Zweier C, Kerr B, et al. Mutations in genes encoding subunits of RNA polymerases I and III cause Treacher Collins syndrome. Nat Genet. 2011;43:20–22. - PubMed
-
- Fokkema IFAC, Taschner PEM, Schaafsma GCP, Celli J, Laros JFJ, den Dunnen JT. LOVD v.2.0: the next generation in gene variant databases. Hum Mutat. 2011;32:557–563. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

