Myocardial strain imaging: how useful is it in clinical decision making?
- PMID: 26508168
- PMCID: PMC4830908
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehv529
Myocardial strain imaging: how useful is it in clinical decision making?
Abstract
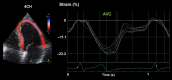
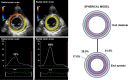
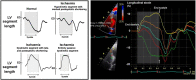
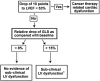
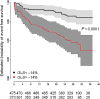
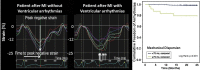
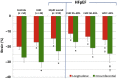
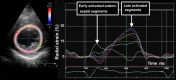
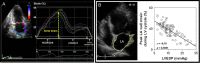
Myocardial strain is a principle for quantification of left ventricular (LV) function which is now feasible with speckle-tracking echocardiography. The best evaluated strain parameter is global longitudinal strain (GLS) which is more sensitive than left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) as a measure of systolic function, and may be used to identify sub-clinical LV dysfunction in cardiomyopathies. Furthermore, GLS is recommended as routine measurement in patients undergoing chemotherapy to detect reduction in LV function prior to fall in LVEF. Intersegmental variability in timing of peak myocardial strain has been proposed as predictor of risk of ventricular arrhythmias. Strain imaging may be applied to guide placement of the LV pacing lead in patients receiving cardiac resynchronization therapy. Strain may also be used to diagnose myocardial ischaemia, but the technology is not sufficiently standardized to be recommended as a general tool for this purpose. Peak systolic left atrial strain is a promising supplementary index of LV filling pressure. The strain imaging methodology is still undergoing development, and further clinical trials are needed to determine if clinical decisions based on strain imaging result in better outcome. With this important limitation in mind, strain may be applied clinically as a supplementary diagnostic method.
Keywords: Cardiomyopathy; Chemotherapy; Heart failure; Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy; Left atrial strain; Left ventricular function; Strain imaging; Ventricular arrhythmia.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Figures






References
-
- Waldman LK, Fung YC, Covell JW. Transmural myocardial deformation in the canine left ventricle. Normal in vivo three-dimensional finite strains. Circ Res 1985;57:152–163. - PubMed
-
- Heimdal A, Stoylen A, Torp H, Skjaerpe T. Real-time strain rate imaging of the left ventricle by ultrasound. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 1998;11:1013–1019. - PubMed
-
- Urheim S, Edvardsen T, Torp H, Angelsen B, Smiseth OA. Myocardial strain by Doppler echocardiography. Validation of a new method to quantify regional myocardial function. Circulation 2000;102:1158–1164. - PubMed
-
- Amundsen BH, Helle-Valle T, Edvardsen T, Torp H, Crosby J, Lyseggen E, Stoylen A, Ihlen H, Lima JA, Smiseth OA, Slordahl SA. Noninvasive myocardial strain measurement by speckle tracking echocardiography: validation against sonomicrometry and tagged magnetic resonance imaging. J Am Coll Cardiol 2006;47:789–793. - PubMed
-
- Jasaityte R, Heyde B, D'Hooge J. Current state of three-dimensional myocardial strain estimation using echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 2013;26:15–28. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

