Development of Aortic Valve Disease in Familial Hypercholesterolemic Swine: Implications for Elucidating Disease Etiology
- PMID: 26508741
- PMCID: PMC4845146
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.115.002254
Development of Aortic Valve Disease in Familial Hypercholesterolemic Swine: Implications for Elucidating Disease Etiology
Erratum in
-
Development of Aortic Valve Disease in Familial Hypercholesterolemic Swine: Implications for Elucidating Disease Etiology.J Am Heart Assoc. 2016 Jan 5;5(1):e002007. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.115.002007. J Am Heart Assoc. 2016. PMID: 26732550 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) is a prevalent hereditary disease associated with increased atherosclerosis and calcific aortic valve disease (CAVD). However, in both FH and non-FH individuals, the role of hypercholesterolemia in the development of CAVD is poorly understood. This study used Rapacz FH (RFH) swine, an established model of human FH, to investigate the role of hypercholesterolemia alone in the initiation and progression of CAVD. The valves of RFH swine have not previously been examined.
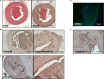
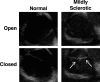
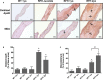
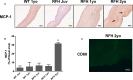
Methods and results: Aortic valve leaflets were isolated from wild-type (0.25- and 1-year-old) and RFH (0.25-, 1-, 2-, and 3-year-old) swine. Adult RFH animals exhibited numerous hallmarks of early CAVD. Significant leaflet thickening was found in adult RFH swine, accompanied by extensive extracellular matrix remodeling, including proteoglycan enrichment, collagen disorganization, and elastin fragmentation. Increased lipid oxidation and infiltration of macrophages were also evident in adult RFH swine. Intracardiac echocardiography revealed mild aortic valve sclerosis in some of the adult RFH animals, but unimpaired valve function. Microarray analysis of valves from adult versus juvenile RFH animals revealed significant upregulation of inflammation-related genes, as well as several commonalities with atherosclerosis and overlap with human CAVD.
Conclusions: Adult RFH swine exhibited several hallmarks of early human CAVD, suggesting potential for these animals to help elucidate CAVD etiology in both FH and non-FH individuals. The development of advanced atherosclerotic lesions, but only early-stage CAVD, in RFH swine supports the hypothesis of an initial shared disease process, with additional stimulation necessary for further progression of CAVD.
Keywords: aortic valve; cardiovascular diseases; hypercholesterolemia.
© 2015 The Authors. Published on behalf of the American Heart Association, Inc., by Wiley Blackwell.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Gene Expression Profiling of Valvular Interstitial Cells in Rapacz Familial Hypercholesterolemic Swine.Genom Data. 2014 Dec 1;2:261-263. doi: 10.1016/j.gdata.2014.08.004. Genom Data. 2014. PMID: 25229013 Free PMC article.
-
NFκB (Nuclear Factor κ-Light-Chain Enhancer of Activated B Cells) Activity Regulates Cell-Type-Specific and Context-Specific Susceptibility to Calcification in the Aortic Valve.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2020 Mar;40(3):638-655. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.119.313248. Epub 2020 Jan 2. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2020. PMID: 31893948 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-Type Transcriptome Atlas of Human Aortic Valves Reveal Cell Heterogeneity and Endothelial to Mesenchymal Transition Involved in Calcific Aortic Valve Disease.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2020 Dec;40(12):2910-2921. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.120.314789. Epub 2020 Oct 22. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2020. PMID: 33086873
-
Molecular and cellular aspects of calcific aortic valve disease.Circ Res. 2013 Jul 5;113(2):198-208. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.113.300155. Circ Res. 2013. PMID: 23833294 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell-matrix interactions in the pathobiology of calcific aortic valve disease: critical roles for matricellular, matricrine, and matrix mechanics cues.Circ Res. 2011 Jun 10;108(12):1510-24. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.110.234237. Circ Res. 2011. PMID: 21659654 Review.
Cited by
-
Disease-inspired tissue engineering: Investigation of cardiovascular pathologies.ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2020 May 11;6(5):2518-2532. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.9b01067. Epub 2019 Oct 29. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2020. PMID: 32974421 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Engineering the aortic valve extracellular matrix through stages of development, aging, and disease.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2021 Dec;161:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2021.07.009. Epub 2021 Jul 30. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2021. PMID: 34339757 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Angiogenic Secretion Profile of Valvular Interstitial Cells Varies With Cellular Sex and Phenotype.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Aug 30;8:736303. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.736303. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34527715 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenome alterations in aortic valve stenosis and its related left ventricular hypertrophy.Clin Epigenetics. 2017 Oct 3;9:106. doi: 10.1186/s13148-017-0406-7. eCollection 2017. Clin Epigenetics. 2017. PMID: 29026447 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Robust Generation of Quiescent Porcine Valvular Interstitial Cell Cultures.J Am Heart Assoc. 2017 Mar 14;6(3):e005041. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.116.005041. J Am Heart Assoc. 2017. PMID: 28292746 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cuchel M, Bruckert E, Ginsberg HN, Raal FJ, Santos RD, Hegele RA, Kuivenhoven JA, Nordestgaard BG, Descamps OS, Steinhagen‐Thiessen E, Tybjaerg‐Hansen A, Watts GF, Averna M, Boileau C, Boren J, Catapano AL, Defesche JC, Hovingh GK, Humphries SE, Kovanen PT, Masana L, Pajukanta P, Parhofer KG, Ray KK, Stalenhoef AF, Stroes E, Taskinen MR, Wiegman A, Wiklund O, Chapman MJ. Homozygous familial hypercholesterolaemia: new insights and guidance for clinicians to improve detection and clinical management. A position paper from the Consensus Panel on Familial Hypercholesterolaemia of the European Atherosclerosis Society. Eur Heart J. 2014;35:2146–2157. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Civeira F; International Panel on Management of Familial H . Guidelines for the diagnosis and management of heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. Atherosclerosis. 2004;173:55–68. - PubMed
-
- Nordestgaard BG, Chapman MJ, Humphries SE, Ginsberg HN, Masana L, Descamps OS, Wiklund O, Hegele RA, Raal FJ, Defesche JC, Wiegman A, Santos RD, Watts GF, Parhofer KG, Hovingh GK, Kovanen PT, Boileau C, Averna M, Boren J, Bruckert E, Catapano AL, Kuivenhoven JA, Pajukanta P, Ray K, Stalenhoef AF, Stroes E, Taskinen MR, Tybjaerg‐Hansen A; European Atherosclerosis Society Consensus P . Familial hypercholesterolaemia is underdiagnosed and undertreated in the general population: guidance for clinicians to prevent coronary heart disease: consensus statement of the European Atherosclerosis Society. Eur Heart J. 2013;34:3478–3490a. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Goldstein JL, Brown MS. Regulation of low‐density lipoprotein receptors: implications for pathogenesis and therapy of hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis. Circulation. 1987;76:504–507. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

