ACE Reduces Metabolic Abnormalities in a High-Fat Diet Mouse Model
- PMID: 26508977
- PMCID: PMC4609822
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/352647
ACE Reduces Metabolic Abnormalities in a High-Fat Diet Mouse Model
Abstract
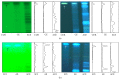
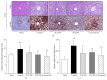
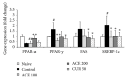
The medicinal plants Artemisia iwayomogi (A. iwayomogi) and Curcuma longa (C. longa) radix have been used to treat metabolic abnormalities in traditional Korean medicine and traditional Chinese medicine (TKM and TCM). In this study we evaluated the effect of the water extract of a mixture of A. iwayomogi and C. longa (ACE) on high-fat diet-induced metabolic syndrome in a mouse model. Four groups of C57BL/6N male mice (except for the naive group) were fed a high-fat diet freely for 10 weeks. Among these, three groups (except the control group) were administered a high-fat diet supplemented with ACE (100 or 200 mg/kg) or curcumin (50 mg/kg). Body weight, accumulation of adipose tissues in abdomen and size of adipocytes, serum lipid profiles, hepatic steatosis, and oxidative stress markers were analyzed. ACE significantly reduced the body and peritoneal adipose tissue weights, serum lipid profiles (total cholesterol and triglycerides), glucose levels, hepatic lipid accumulation, and oxidative stress markers. ACE normalized lipid synthesis-associated gene expressions (peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma, PPARγ; fatty acid synthase, FAS; sterol regulatory element-binding transcription factor-1c, SREBP-1c; and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha, PPARα). The results from this study suggest that ACE has the pharmaceutical potential reducing the metabolic abnormalities in an animal model.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Synergistic effects of Artemisia iwayomogi and Curcuma longa radix on high-fat diet-induced hyperlipidemia in a mouse model.J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Sep 15;173:217-24. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2015.07.021. Epub 2015 Jul 23. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26212022
-
Anti-atherosclerosis and hyperlipidemia effects of herbal mixture, Artemisia iwayomogi Kitamura and Curcuma longa Linne, in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice.J Ethnopharmacol. 2014 Apr 11;153(1):142-50. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.01.039. Epub 2014 Feb 7. J Ethnopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24508858
-
Caulerpa okamurae extract inhibits adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes and prevents high-fat diet-induced obesity in C57BL/6 mice.Nutr Res. 2017 Nov;47:44-52. doi: 10.1016/j.nutres.2017.09.002. Epub 2017 Sep 14. Nutr Res. 2017. PMID: 29241577
-
Eburicoic Acid, a Triterpenoid Compound from Antrodia camphorata, Displays Antidiabetic and Antihyperlipidemic Effects in Palmitate-Treated C2C12 Myotubes and in High-Fat Diet-Fed Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Nov 2;18(11):2314. doi: 10.3390/ijms18112314. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29099085 Free PMC article.
-
Polygala tenuifolia extract inhibits lipid accumulation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes and high-fat diet-induced obese mouse model and affects hepatic transcriptome and gut microbiota profiles.Food Nutr Res. 2017 Oct 5;61(1):1379861. doi: 10.1080/16546628.2017.1379861. eCollection 2017. Food Nutr Res. 2017. PMID: 29056891 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Hot Water Extract of Curcuma longa L. Improves Serum Inflammatory Markers and General Health in Subjects with Overweight or Prehypertension/Mild Hypertension: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial.Nutrients. 2019 Aug 7;11(8):1822. doi: 10.3390/nu11081822. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31394768 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Pistachio Consumption Prevents and Improves Lipid Dysmetabolism by Reducing the Lipid Metabolizing Gene Expression in Diet-Induced Obese Mice.Nutrients. 2018 Dec 1;10(12):1857. doi: 10.3390/nu10121857. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 30513740 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic Review of Polyherbal Combinations Used in Metabolic Syndrome.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Oct 7;12:752926. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.752926. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34690784 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Hot Water Extract of Curcuma longa L. Improves Fasting Serum Glucose Levels in Participants with Low-Grade Inflammation: Reanalysis of Data from Two Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trials.Nutrients. 2022 Sep 13;14(18):3763. doi: 10.3390/nu14183763. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36145139 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

