The Interaction between Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Parkinson's Disease: Possible Mechanisms and Implications for Cognitive Function
- PMID: 26509097
- PMCID: PMC4609874
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/849472
The Interaction between Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Parkinson's Disease: Possible Mechanisms and Implications for Cognitive Function
Abstract
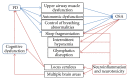
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a relentlessly progressive neurodegenerative disorder associated with hallmark motor and nonmotor symptoms (NMS) such as sleep disturbances and cognitive dysfunction. While dopaminergic treatments have improved the motor aspects of PD, progression remains inevitable. Research has recently increasingly focused on strategies to modify disease progression and on nonmotor manifestations of PD, given their impact on patients' quality of life. Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a treatable sleep disorder, common in the general population, associated with excessive daytime sleepiness and neurocognitive deficits. Neuroimaging has demonstrated structural and functional changes in OSA patients; in animal models, OSA causes brain inflammation and oxidative injury, including in key areas involved in PD pathophysiology such as locus coeruleus. The prevalence of OSA in PD has been variable in studies to date, and potential consequences and interrelationship between the two disorders have not been well studied. There is however emerging evidence that OSA is associated with increased NMS in PD, particularly cognitive dysfunction. This review focuses on the possible interrelationship between OSA and PD. Mechanisms promoting OSA in PD will be reviewed, as well as mechanisms whereby OSA can affect the neurodegenerative process in PD.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of Obstructive Sleep Apnea on Cognitive and Motor Functions in Parkinson's Disease.Mov Disord. 2021 Mar;36(3):570-580. doi: 10.1002/mds.28412. Epub 2020 Dec 9. Mov Disord. 2021. PMID: 33296545
-
Reduced cognitive function in patients with Parkinson disease and obstructive sleep apnea.Neurology. 2017 Mar 21;88(12):1120-1128. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000003738. Epub 2017 Feb 22. Neurology. 2017. PMID: 28228566
-
Obstructive sleep apnea in Parkinson's disease: A prevalent, clinically relevant and treatable feature.Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2023 Oct;115:105790. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2023.105790. Epub 2023 Aug 1. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2023. PMID: 37541789 Review.
-
Nonmotor symptoms in nursing home residents with Parkinson's disease: prevalence and effect on quality of life.J Am Geriatr Soc. 2013 Oct;61(10):1714-21. doi: 10.1111/jgs.12458. Epub 2013 Oct 1. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2013. PMID: 24117286
-
Neurological Deficits in Obstructive Sleep Apnea.Curr Treat Options Neurol. 2017 Apr;19(4):16. doi: 10.1007/s11940-017-0451-8. Curr Treat Options Neurol. 2017. PMID: 28374233 Review.
Cited by
-
Parkinson's disease and obstructive sleep apnea.EXCLI J. 2021 Feb 23;20:490. doi: 10.17179/excli2021-3359. eCollection 2021. EXCLI J. 2021. PMID: 33746674 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Disruption of Circadian Rhythm Genes in Obstructive Sleep Apnea Patients-Possible Mechanisms Involved and Clinical Implication.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 10;23(2):709. doi: 10.3390/ijms23020709. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35054894 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of Rapid Eye Movement Sleep Behavior Disorder on Obstructive Sleep Apnea Severity and Cognition of Parkinson's Disease Patients.Chin Med J (Engl). 2018 Apr 20;131(8):899-906. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.229888. Chin Med J (Engl). 2018. PMID: 29664048 Free PMC article.
-
Logopenic aphasia due to Lewy body disease dramatically improved with donepezil.eNeurologicalSci. 2020 May 8;19:100241. doi: 10.1016/j.ensci.2020.100241. eCollection 2020 Jun. eNeurologicalSci. 2020. PMID: 32455171 Free PMC article.
-
Nature's Remedies: Exploring the Potential of Propolis to Alleviate Non-Motor Manifestations of Parkinson's Disease.Molecules. 2025 Apr 8;30(8):1672. doi: 10.3390/molecules30081672. Molecules. 2025. PMID: 40333577 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Beebe D. W., Groesz L., Wells C., Nichols A., McGee K. The neuropsychological effects of obstructive sleep apnea: a meta-analysis of norm-referenced and case-controlled data. Sleep. 2003;26(3):298–307. - PubMed
-
- Gaudette E., Kimoff R. J. Pathophysiology of obstructive sleep apnoea. In: McNicholas W., Bonsignore M., editors. European Respiratory Monograph. 2011.
-
- Punjabi N. M., Newman A. B., Young T. B., Resnick H. E., Sanders M. H. Sleep-disordered breathing and cardiovascular disease: an outcome-based definition of hypopneas. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 2008;177(10):1150–1155. doi: 10.1164/rccm.200712-1884oc. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources