Prognosis of Early-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma: The Clinical Implications of Substages of Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer System Based on a Cohort of 1265 Patients
- PMID: 26512620
- PMCID: PMC4985433
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000001929
Prognosis of Early-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma: The Clinical Implications of Substages of Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer System Based on a Cohort of 1265 Patients
Abstract
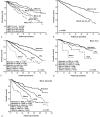
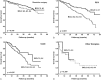
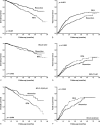
The prognostic implication of Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) substages in Asian patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is still obscure.The aim to this study is to compare the prognoses among HCC patients in different substages of the BCLC stage 0 and A.We enrolled 1265 treatment-naive HCC patients with BCLC stage 0 or A from 2007 to 2014. Factors in terms of prognoses were analyzed by multivariate analysis.There were 184, 446, 271, 92, and 272 patients in substage 0, A1, A2, A3, and A4, respectively. After a median follow-up period of 21.0 months, patients in stages 0 and A1 had comparable prognoses (P = 0.136). Both of them had significantly higher overall survival rates than those in stages A2-A4 (all P < 0.001). Multivariate analysis revealed that the factors associated with mortality were serum albumin ≤3.5 g/dL (hazard ratio [HR] 1.459), alpha-fetoprotein >20 ng/mL (HR 1.863), tumor size >3 cm (HR 1.542), BCLC stage A2-A4 (HR 1.488), and treatment modality. Surgical resection had the highest overall survival rate followed by radiofrequency ablation (RFA) (HR 1.598), transarterial chemoembolization (HR 2.224), and other treatments (HR 3.707). Verus patients receiving RFA, those who underwent resection had a higher overall survival rate and lower recurrence rate especially in BCLC stages A2-A4.The BCLC-staging system provided good prognostic stratification for early-stage HCC. Patients with a single tumor >2 cm but without portal hypertension or jaundice had similar prognosis to those in BCLC stage 0. Curative therapies-especially hepatic resection-are suggested in early-stage HCC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- Forner A, Llovet JM, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet 2012; 379:1245–1255. - PubMed
-
- El-Serag HB. Hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med 2011; 365:1118–1127. - PubMed
-
- Chen PH, Kao WY, Chiou YY, et al. Comparison of prognosis by viral etiology in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after radiofrequency ablation. Ann Hepatol 2013; 12:263–273. - PubMed
-
- Su CW, Wu CY, Hung HH, et al. Differential roles of serum hepatitis B virus DNA and hepatitis B surface antigen level in predicting virological breakthrough in patients receiving lamivudine therapy. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2013; 28:1849–1858. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

