Liver transplantation: intraoperative changes in coagulation factors in 100 first transplants
- PMID: 2651269
- PMCID: PMC3032392
- DOI: 10.1002/hep.1840090509
Liver transplantation: intraoperative changes in coagulation factors in 100 first transplants
Abstract
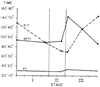
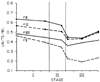
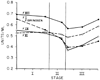
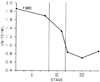
Six intraoperative blood samples were obtained at intervals from each of 100 individuals undergoing their first liver transplants. The patients fell into the following diagnostic categories: postnecrotic cirrhosis 28, primary biliary cirrhosis 20, sclerosing cholangitis 19, miscellaneous diseases 14, carcinoma/neoplasia 12 and fulminant hepatitis 7. Coagulation factor values in the initial (baseline) blood samples varied by patient diagnosis. In general, all factor levels were reduced except factor VIII:C, which was increased to almost twice normal. The slight intraoperative changes in factors II, VII, IX, X, XI and XII suggested that a steady-state relationship existed between depletion (consumption/bleeding) and repletion (transfusion, transit from extra- to intravascular space), even in the anhepatic state. In contrast, there were rapid and very significant falls in factor VIII and fibrinogen and a less pronounced decrease in factor V, all reaching their nadirs in early to mid-Stage III. The cause of these coagulation changes appears to be activation of the fibrinolytic system.
Figures
References
-
- Kang YG. Monitoring and treatment of coagulation. In: Winter PM, Kang YG, editors. Hepatic transplantation: anesthetic and perioperative management. New York: Praeger Publishers; 1986. pp. 151–173.
-
- Lewis JH. Coagulation defects. JAMA. 1961;178:1014–1020. - PubMed
-
- Lewis JH. Hemostasis and hemorrhage. Sci Clin. 1971;1:l–66.
-
- Lewis JH, Spero JA, Hasiba U. Bleeding disorders. Garden City, New York: Medical Examination Publishing Co., Inc.; 1978. Diagnostic methods: laboratory tests; pp. 22–34.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical