Celecoxib increases lung cancer cell lysis by lymphokine-activated killer cells via upregulation of ICAM-1
- PMID: 26513172
- PMCID: PMC4770776
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.5745
Celecoxib increases lung cancer cell lysis by lymphokine-activated killer cells via upregulation of ICAM-1
Abstract
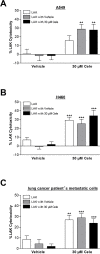
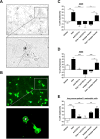
The antitumorigenic mechanism of the selective cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitor celecoxib is still a matter of debate. Using lung cancer cell lines (A549, H460) and metastatic cells derived from a lung cancer patient, the present study investigates the impact of celecoxib on the expression of intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) and cancer cell lysis by lymphokine-activated killer (LAK) cells. Celecoxib, but not other structurally related selective COX-2 inhibitors (i.e., etoricoxib, rofecoxib, valdecoxib), was found to cause a substantial upregulation of ICAM-1 protein levels. Likewise, ICAM-1 mRNA expression was increased by celecoxib. Celecoxib enhanced the susceptibility of cancer cells to be lysed by LAK cells with the respective effect being reversed by a neutralizing ICAM-1 antibody. In addition, enhanced killing of celecoxib-treated cancer cells was reversed by preincubation of LAK cells with an antibody to lymphocyte function associated antigen 1 (LFA-1), suggesting intercellular ICAM-1/LFA-1 crosslink as crucial event within this process. Finally, celecoxib elicited no significant increase of LAK cell-mediated lysis of non-tumor bronchial epithelial cells, BEAS-2B, associated with a far less ICAM-1 induction as compared to cancer cells. Altogether, our data demonstrate celecoxib-induced upregulation of ICAM-1 on lung cancer cells to be responsible for intercellular ICAM-1/LFA-1 crosslink that confers increased cancer cell lysis by LAK cells. These findings provide proof for a novel antitumorigenic mechanism of celecoxib.
Keywords: celecoxib; immune surveillance; intercellular adhesion molecule 1; lung cancer cells; lymphokine-activated killer cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors indicate no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Steinbach G, Lynch PM, Phillips RK, Wallace MH, Hawk E, Gordon GB, Wakabayashi N, Saunders B, Shen Y, Fujimura T, Su LK, Levin B, Godio L, et al. The effect of celecoxib, a cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, in familial adenomatous polyposis. N Engl J Med. 2000;342:1946–1952. - PubMed
-
- Edelman MJ, Watson D, Wang X, Morrison C, Kratzke RA, Jewell S, Hodgson L, Mauer AM, Gajra A, Masters GA, Bedor M, Vokes EE, Green MJ. Eicosanoid modulation in advanced lung cancer: cyclooxygenase-2 expression is a positive predictive factor for celecoxib + chemotherapy - Cancer and Leukemia Group B Trial 30203. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26:848–855. - PubMed
-
- Wang Z, Duan J, Guo Q, Wei Z, Xue W, Wu M, Zhao J, Yang L, An T, Liu X, Wang J. A phase II clinical trial of celecoxib combined with platinum-based chemotherapy in the treatment of patients with advanced NSCLC as first-line treatment. Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 2008;11:425–430. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

