Probing Difference in Binding Modes of Inhibitors to MDMX by Molecular Dynamics Simulations and Different Free Energy Methods
- PMID: 26513747
- PMCID: PMC4625964
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0141409
Probing Difference in Binding Modes of Inhibitors to MDMX by Molecular Dynamics Simulations and Different Free Energy Methods
Abstract
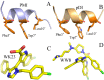
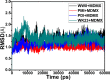
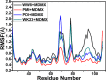
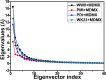
The p53-MDMX interaction has attracted extensive attention of anti-cancer drug development in recent years. This current work adopted molecular dynamics (MD) simulations and cross-correlation analysis to investigate conformation changes of MDMX caused by inhibitor bindings. The obtained information indicates that the binding cleft of MDMX undergoes a large conformational change and the dynamic behavior of residues obviously change by the presence of different structural inhibitors. Two different methods of binding free energy predictions were employed to carry out a comparable insight into binding mechanisms of four inhibitors PMI, pDI, WK23 and WW8 to MDMX. The data show that the main factor controlling the inhibitor bindings to MDMX arises from van der Waals interactions. The binding free energies were further divided into contribution of each residue and the derived information gives a conclusion that the hydrophobic interactions, such as CH-CH, CH-π and π-π interactions, are responsible for the inhibitor associations with MDMX.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- Boettger V, Boettger A, Garcia-Echeverria C, Ramos Y, van der Eb AJ, Jochemsen AG, et al. Comparative study of the p53-mdm2 and p53-MDMX interfaces. Oncogene. 1999;18(1):189–99. - PubMed
-
- Amadei A, Linssen A, Berendsen HJC. Essential dynamics of proteins. Proteins. 2004;17(4):412–25. - PubMed
-
- Vousden KH, Lane DP. p53 in health and disease. Nat Rev Mol Cel Biol. 2007;8(4):275–83. - PubMed
-
- Marine JCW, Dyer MA, Jochemsen AG. MDMX: from bench to bedside. J Cell Sci. 2007;120(3):371–8. - PubMed
-
- Vassilev LT, Vu BT, Graves B, Carvajal D, Podlaski F, Filipovic Z, et al. In vivo activation of the p53 pathway by small-molecule antagonists of MDM2. Science. 2004;303(5659):844–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

