Neuropathology of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Its Variants
- PMID: 26515626
- PMCID: PMC4628785
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ncl.2015.07.012
Neuropathology of Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Its Variants
Abstract
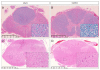
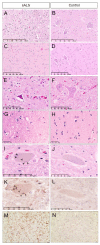
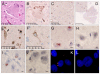
The neuropathologic molecular signature common to almost all sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and most familial ALS is TDP-43 immunoreactive neuronal cytoplasmic inclusions. The neuropathologic and molecular neuropathologic features of ALS variants, primarily lateral sclerosis and progressive muscular atrophy, are less certain but also seem to share the primary features of ALS. Genetic causes, including mutations in SOD1, TDP-43, FUS, and C9orf72, all have distinctive molecular neuropathologic signatures. Neuropathology will continue to play an increasingly key role in solving the puzzle of ALS pathogenesis.
Keywords: Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; C9orf72; Motor neuron degeneration; Neuropathology; TDP-43.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Tyler HR, Shefner J. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Handb Clin Neurol. 1991;15:169–215.
-
- Aran F. Recherches sur une maladie non encore décrite du système musculaire (atrophie musculaire progressive) Arch Gen Med. 1850;24:172.
-
- Cruveilhier J. Sur la paralysie musculaire progressive atrophique. Arch Gen Med. 1853;91:561–603.
-
- Duchenne de Boulogne G. Recherches électro-physiologiques et thérapeutiques. Comp Rend Seances Acad Sci. 1851;32:506.
-
- Charcot J-M, Joffroy A. Deux cas d’atrophie musculaire progressive: avec lésions de la substance grise et des faisceaux antérolatéraux de la moelle épinière. Masson; 1869.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

