Long non-coding RNAs in corticogenesis: deciphering the non-coding code of the brain
- PMID: 26516210
- PMCID: PMC4687686
- DOI: 10.15252/embj.201592655
Long non-coding RNAs in corticogenesis: deciphering the non-coding code of the brain
Abstract
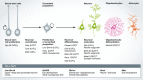
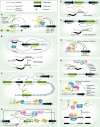
Evidence on the role of long non-coding (lnc) RNAs has been accumulating over decades, but it has been only recently that advances in sequencing technologies have allowed the field to fully appreciate their abundance and diversity. Despite this, only a handful of lncRNAs have been phenotypically or mechanistically studied. Moreover, novel lncRNAs and new classes of RNAs are being discovered at growing pace, suggesting that this class of molecules may have functions as diverse as protein-coding genes. Interestingly, the brain is the organ where lncRNAs have the most peculiar features including the highest number of lncRNAs that are expressed, proportion of tissue-specific lncRNAs and highest signals of evolutionary conservation. In this work, we critically review the current knowledge about the steps that have led to the identification of the non-coding transcriptome including the general features of lncRNAs in different contexts in terms of both their genomic organisation, evolutionary origin, patterns of expression, and function in the developing and adult mammalian brain.
Keywords: brain development; long non‐coding RNAs; neural stem cells.
© 2015 The Authors.
Figures

References
-
- Adachi N, Lieber MR (2002) Bidirectional gene organization: a common architectural feature of the human genome. Cell 109: 807–809 - PubMed
-
- Andersson R, Gebhard C, Miguel‐Escalada I, Hoof I, Bornholdt J, Boyd M, Chen Y, Zhao X, Schmidl C, Suzuki T, Ntini E, Arner E, Valen E, Li K, Schwarzfischer L, Glatz D, Raithel J, Lilje B, Rapin N, Bagger FO et al (2014) An atlas of active enhancers across human cell types and tissues. Nature 507: 455–461 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Andrews SJ, Rothnagel JA (2014) Emerging evidence for functional peptides encoded by short open reading frames. Nat Rev Genet 15: 193–204 - PubMed
-
- Aprea J, Prenninger S, Dori M, Ghosh T, Monasor LS, Wessendorf E, Zocher S, Massalini S, Alexopoulou D, Lesche M, Dahl A, Groszer M, Hiller M, Calegari F (2013) Transcriptome sequencing during mouse brain development identifies long non‐coding RNAs functionally involved in neurogenic commitment. EMBO J 32: 3145–3160 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

