Use of the RISK21 roadmap and matrix: human health risk assessment of the use of a pyrethroid in bed netting
- PMID: 26517449
- PMCID: PMC4732465
- DOI: 10.3109/10408444.2015.1082974
Use of the RISK21 roadmap and matrix: human health risk assessment of the use of a pyrethroid in bed netting
Abstract
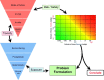
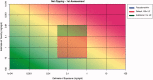
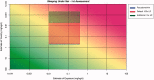
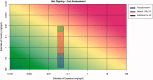
The HESI-coordinated RISK21 roadmap and matrix are tools that provide a transparent method to compare exposure and toxicity information and assess whether additional refinement is required to obtain the necessary precision level for a decision regarding safety. A case study of the use of a pyrethroid, "pseudomethrin," in bed netting to control malaria is presented to demonstrate the application of the roadmap and matrix. The evaluation began with a problem formulation step. The first assessment utilized existing information pertaining to the use and the class of chemistry. At each stage of the step-wise approach, the precision of the toxicity and exposure estimates were refined as necessary by obtaining key data which enabled a decision on safety to be made efficiently and with confidence. The evaluation demonstrated the concept of using existing information within the RISK21 matrix to drive the generation of additional data using a value-of-information approach. The use of the matrix highlighted whether exposure or toxicity required further investigation and emphasized the need to address the default uncertainty factor of 100 at the highest tier of the evaluation. It also showed how new methodology such as the use of in vitro studies and assays could be used to answer the specific questions which arise through the use of the matrix. The matrix also serves as a useful means to communicate progress to stakeholders during an assessment of chemical use.
Keywords: Integrated testing strategy; pyrethroid; risk assessment; tiered approach.
Figures
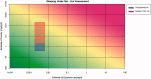
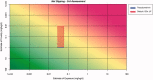
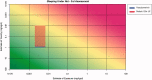
References
-
- Barlow S, Sullivan F, Lines J. Risk assessment of the use of deltalmethrin on bednets for the prevention of malaria. Food Chem Toxicol. 2001;39:407–422. - PubMed
-
- Bitsch A, Jacobi S, Melber C, Wahnschaffe U, Simetska N, Mangelsdorf I. REPDOSE: a database on repeated dose toxicity studies of commercial chemicals – a multifunctional tool. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2006;46:202–210. - PubMed
-
- California EPA. Deltamethrin risk characterization. Sacramento, CA: California Environmental Protection Agency, Health Assessment Section, Medical Toxicology Branch, Department of Pesticide Regulation; 2000.
-
- Dorne JL, Renwick AG. The refinement of uncertainty/safety factors in risk assessment by the incorporation of data on toxicokinetic variability in humans. Toxicol Sci. 2005;86:20–26. - PubMed
-
- Embry M, Bachman A, Bell D, Boobis A, Cohen S, Dellarco M, Dewhurst I. Risk assessment in the 21st century (RISK21): roadmap and matrix. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2014;44(Suppl 3):6–16. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
