Tackling malnutrition: a systematic review of 15-year research evidence from INDEPTH health and demographic surveillance systems
- PMID: 26519130
- PMCID: PMC4627942
- DOI: 10.3402/gha.v8.28298
Tackling malnutrition: a systematic review of 15-year research evidence from INDEPTH health and demographic surveillance systems
Abstract
Background: Nutrition is the intake of food in relation to the body's dietary needs. Malnutrition results from the intake of inadequate or excess food. This can lead to reduced immunity, increased susceptibility to disease, impaired physical and mental development, and reduced productivity.
Objective: To perform a systematic review to assess research conducted by the International Network for the Demographic Evaluation of Populations and their Health (INDEPTH) of health and demographic surveillance systems (HDSSs) over a 15-year period on malnutrition, its determinants, the effects of under and over nutrition, and intervention research on malnutrition in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs).
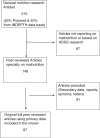
Methods: Relevant publication titles were uploaded onto the Zotero research tool from different databases (60% from PubMed). Using the keywords 'nutrition', 'malnutrition', 'over and under nutrition', we selected publications that were based only on data generated through the longitudinal HDSS platform. All titles and abstracts were screened to determine inclusion eligibility and full articles were independently assessed according to inclusion/exclusion criteria. For inclusion in this study, papers had to cover research on at least one of the following topics: the problem of malnutrition, its determinants, its effects, and intervention research on malnutrition. One hundred and forty eight papers were identified and reviewed, and 67 were selected for this study.
Results: The INDEPTH research identified rising levels of overweight and obesity, sometimes in the same settings as under-nutrition. Urbanisation appears to be protective against under-nutrition, but it heightens the risk of obesity. Appropriately timed breastfeeding interventions were protective against malnutrition.
Conclusions: Although INDEPTH has expanded the global knowledge base on nutrition, many questions remain unresolved. There is a need for more investment in nutrition research in LMICs in order to generate evidence to inform policies in these settings.
Keywords: LMICs; health and demographic surveillance system; low- and middle-income countries; malnutrition; nutrition; overweight; under and over nutrition.
Figures
References
-
- Lagua RT, Claudio VS. Nutrition and diet therapy reference dictionary. New York: Chapman & Hall; 1995.
-
- World Health Organization. Turning the tide of malnutrition: responding to the challenge of the 21st century. Geneva: WHO; 2000. Available from: http://www.who.int/nut/documents/nhd_brochure.pdf?ua=1.
-
- Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations. The state of food insecurity in the world. Rome, Italy: FAO; 2011.
-
- World Health Organization. MDG1: eradicate extreme poverty and hunger. 2013. Available from: http://www.who.int/topics/millennium_development_goals/hunger/en/index.html [cited 12 June 2015].
-
- Nemer L, Gelband H, Jha P. CMH working paper no WG5:11. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2001. Commission on Macroeconomics and Health. The evidence base for interventions to reduce malnutrition in children under five and school-age children in low- and middle-income countries.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical