Lipid mediator profile in vernix caseosa reflects skin barrier development
- PMID: 26521946
- PMCID: PMC4629127
- DOI: 10.1038/srep15740
Lipid mediator profile in vernix caseosa reflects skin barrier development
Abstract
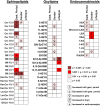
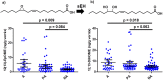
Vernix caseosa (VC) is a protective layer that covers the skin of most human newborns. This study characterized the VC lipid mediator profile, and examined its relationship to gestational period, gender of the newborn and maternal lifestyle. VC collected at birth from 156 newborns within the ALADDIN birth cohort was analyzed and 3 different groups of lipid mediators (eicosanoids and related oxylipin analogs, endocannabinoids and sphingolipids) were screened using LC-MS/MS. A total of 54 compounds were detected in VC. A number of associations between lipid mediators and the gestational period were observed, including increases in the ceramide to sphingomyelin ratio as well as the endocannabinoids anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol. Gender-specific differences in lipid mediator levels were observed for all 3 lipid classes. In addition, levels of the linoleic acid oxidation products 9(10)-epoxy-12Z-octadecenoic and 12(13)-epoxy-9Z-octadecenoic acid (EpOMEs) as well as 12,13-dihydroxy-9Z-octadecenoic acid (DiHOME) were increased in VC of children from mothers with an anthroposophic lifestyle. Accordingly, VC was found to be rich in multiple classes of bioactive lipid mediators, which evidence lifestyle, gender and gestational week dependencies. Levels of lipid mediators in VC may therefore be useful as early stage non-invasive markers of the development of the skin as a protective barrier.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Lanolin-derived lipid mixtures mimic closely the lipid composition and organization of vernix caseosa lipids.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008 Oct;1778(10):2350-60. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2008.06.017. Epub 2008 Jul 4. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008. PMID: 18655769
-
Vernix caseosa reveals mechanistic clues linking maternal obesity to atopic dermatitis pathogenesis.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2024 Mar;153(3):860-867.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2023.09.042. Epub 2023 Dec 2. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38048884
-
Applying a vernix caseosa based formulation accelerates skin barrier repair by modulating lipid biosynthesis.J Lipid Res. 2018 Feb;59(2):250-260. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M079186. Epub 2017 Dec 7. J Lipid Res. 2018. PMID: 29217624 Free PMC article.
-
Vernix caseosa in neonatal adaptation.J Perinatol. 2005 Jul;25(7):440-6. doi: 10.1038/sj.jp.7211305. J Perinatol. 2005. PMID: 15830002 Review.
-
Biology of the vernix caseosa: A review.J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2019 Nov;45(11):2145-2149. doi: 10.1111/jog.14103. Epub 2019 Sep 10. J Obstet Gynaecol Res. 2019. PMID: 31507021 Review.
Cited by
-
Epidermal Immunity and Function: Origin in Neonatal Skin.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Jun 8;9:894496. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.894496. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35755808 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microbiome in the Gut-Skin Axis in Atopic Dermatitis.Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2018 Jul;10(4):354-362. doi: 10.4168/aair.2018.10.4.354. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2018. PMID: 29949831 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DERMATOSES IN THE EARLY NEONATAL PERIOD: THEIR ASSOCIATION WITH NEONATAL, OBSTETRIC AND DEMOGRAPHIC VARIABLES.Rev Paul Pediatr. 2019 Jun 3;37(3):297-304. doi: 10.1590/1984-0462/;2019;37;3;00012. eCollection 2019. Rev Paul Pediatr. 2019. PMID: 31166467 Free PMC article.
-
Brown Fat-Activating Lipokine 12,13-diHOME in Human Milk Is Associated With Infant Adiposity.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021 Jan 23;106(2):e943-e956. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgaa799. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2021. PMID: 33135728 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Endocrine Role for the BAT-Released Lipokine 12,13-diHOME to Mediate Cardiac Function.Circulation. 2021 Jan 12;143(2):145-159. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.120.049813. Epub 2020 Oct 27. Circulation. 2021. PMID: 33106031 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hoeger P. H. et al. Epidermal barrier lipids in human vernix caseosa: corresponding ceramide pattern in vernix and fetal skin. Br J Dermatol 146, 194–201 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Visscher M. O. et al. Vernix caseosa in neonatal adaptation. J Perinatol 25, 440–446 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Kendall A. C. & Nicolaou A. Bioactive lipid mediators in skin inflammation and immunity. Prog Lipid Res 52, 141–164 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Nicolaou A. Eicosanoids in skin inflammation. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 88, 131–138 (2013). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

