Stimulation of the wrist acupuncture point PC6 for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting
- PMID: 26522652
- PMCID: PMC4679372
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003281.pub4
Stimulation of the wrist acupuncture point PC6 for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting
Update in
-
Stimulation of the wrist acupuncture point PC6 for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025 Sep 12;9(9):CD003281. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003281.pub5. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2025. PMID: 40938065
Abstract
Background: Postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV) are common complications following surgery and anaesthesia. Antiemetic drugs are only partially effective in preventing PONV. An alternative approach is to stimulate the PC6 acupoint on the wrist. This is an update of a Cochrane review first published in 2004, updated in 2009 and now in 2015.
Objectives: To determine the effectiveness and safety of PC6 acupoint stimulation with or without antiemetic drug versus sham or antiemetic drug for the prevention of PONV in people undergoing surgery.
Search methods: We searched the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) (Cochrane Library, Issue 12, 2014), MEDLINE (January 2008 to December 2014), EMBASE (January 2008 to December 2014), ISI Web of Science (January 2008 to December 2014), World Health Organization Clinical Trials Registry, ClinicalTrials.gov, and reference lists of articles to identify additional studies. We applied no language restrictions.
Selection criteria: All randomized trials of techniques that stimulated the PC6 acupoint compared with sham treatment or drug therapy, or combined PC6 acupoint and drug therapy compared to drug therapy, for the prevention of PONV. Interventions used in these trials included acupuncture, electro-acupuncture, transcutaneous electrical acupoint stimulation, transcutaneous nerve stimulation, laser stimulation, capsicum plaster, acu-stimulation device, and acupressure in people undergoing surgery. Primary outcomes were the incidences of nausea and vomiting after surgery. Secondary outcomes were the need for rescue antiemetic therapy and adverse effects.
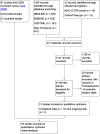
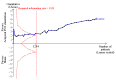
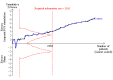
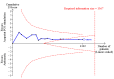
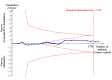
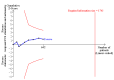
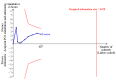
Data collection and analysis: Two review authors independently extracted the data and assessed the risk of bias domains for each trial. We used a random-effects model and reported risk ratio (RR) with associated 95% confidence interval (95% CI). We used trial sequential analyses to help provide information on when we had reached firm evidence in cumulative meta-analyses of the primary outcomes, based on a 30% risk ratio reduction in PONV.
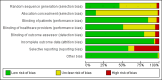
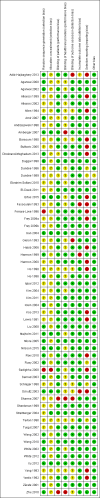
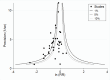
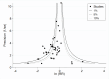
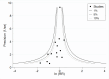
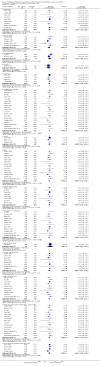
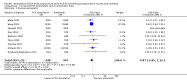
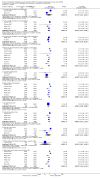
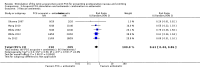
Main results: We included 59 trials involving 7667 participants. We rated two trials at low risk of bias in all domains (selection, attrition, reporting, blinding and other). We rated 25 trials at high risk in one or more risk-of-bias domains. Compared with sham treatment, PC6 acupoint stimulation significantly reduced the incidence of nausea (RR 0.68, 95% CI 0.60 to 0.77; 40 trials, 4742 participants), vomiting (RR 0.60, 95% CI 0.51 to 0.71; 45 trials, 5147 participants) and the need for rescue antiemetics (RR 0.64, 95% CI 0.55 to 0.73; 39 trials, 4622 participants). As heterogeneity among trials was substantial and there were study limitations, we rated the quality of evidence as low. Using trial sequential analysis, the required information size and boundary for benefit were reached for both primary outcomes.PC6 acupoint stimulation was compared with six different types of antiemetic drugs (metoclopramide, cyclizine, prochlorperazine, droperidol. ondansetron and dexamethasone). There was no difference between PC6 acupoint stimulation and antiemetic drugs in the incidence of nausea (RR 0.91, 95% CI 0.75 to 1.10; 14 trials, 1332 participants), vomiting (RR 0.93, 95% CI 0.74 to 1.17; 19 trials, 1708 participants), or the need for rescue antiemetics (RR 0.87, 95% CI 0.65 to 1.16; 9 trials, 895 participants). We rated the quality of evidence as moderate, due to the study limitations. Using trial sequential analyses, the futility boundary was crossed before the required information size was surpassed for both primary outcomes.Compared to antiemetic drugs, the combination of PC6 acupoint stimulation and antiemetic therapy reduced the incidence of vomiting (RR 0.56, 95% CI 0.35 to 0.91; 9 trials, 687 participants) but not nausea (RR 0.79, 95% CI 0.55 to 1.13; 8 trials, 642 participants). We rated the quality of evidence as very low, due to substantial heterogeneity among trials, study limitations and imprecision. Using trial sequential analysis, none of the boundaries for benefit, harm or futility were crossed for PONV. The need for rescue antiemetic was lower in the combination PC6 acupoint stimulation and antiemetic group than the antiemetic group (RR 0.61, 95% CI 0.44 to 0.86; 5 trials, 419 participants).The side effects associated with PC6 acupoint stimulation were minor, transient and self-limiting (e.g. skin irritation, blistering, redness and pain) in 14 trials. Publication bias was not apparent in the contour-enhanced funnel plots.
Authors' conclusions: There is low-quality evidence supporting the use of PC6 acupoint stimulation over sham. Compared to the last update in 2009, no further sham comparison trials are needed. We found that there is moderate-quality evidence showing no difference between PC6 acupoint stimulation and antiemetic drugs to prevent PONV. Further PC6 acupoint stimulation versus antiemetic trials are futile in showing a significant difference, which is a new finding in this update. There is inconclusive evidence supporting the use of a combined strategy of PC6 acupoint stimulation and antiemetic drug over drug prophylaxis, and further high-quality trials are needed.
Conflict of interest statement
Anna Lee has no conflicts relating to this review. Simon KC Chan has no conflicts relating to this review. Lawrence TY Fan has no conflicts relating to this review.
Figures

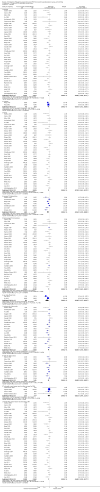
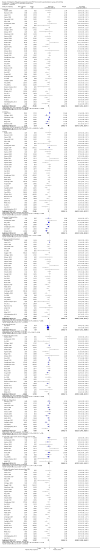
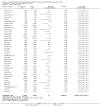
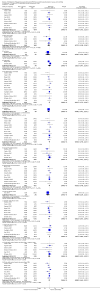

Update of
-
Stimulation of the wrist acupuncture point P6 for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009 Apr 15;(2):CD003281. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003281.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015 Nov 02;(11):CD003281. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD003281.pub4. PMID: 19370583 Free PMC article. Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Adib‐Hajbaghery 2013 {published data only}
Agarwal 2000 {published data only}
-
- Agarwal A, Pathak A, Gaur A. Acupressure wristbands do not prevent postoperative nausea and vomiting after urological endoscopic surgery. Canadian Journal of Anaesthesia 2000;47(4):319‐24. [PUBMED: 10764175] - PubMed
Agarwal 2002 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Agarwal A, Bose N, Gaur A, Singh U, Gupta MK, Singh D. Acupressure and ondansetron for postoperative nausea and vomiting after laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Canadian Journal of Anesthesia 2002;49(6):554‐60. [PUBMED: 12067865] - PubMed
Alkaissi 1999 {published data only}
-
- Alkaissi A, Stålnert M, Kalman S. Effect and placebo effect of acupressure (P6) on nausea and vomiting after outpatient gynaecological surgery. Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica 1999;43(3):270‐4. [PUBMED: 10081532] - PubMed
Alkaissi 2002 {published data only}
-
- Alkaissi A, Evertsson K, Johnsson V, Ofenbartl L, Kalman S. P6 acupressure may relieve nausea and vomiting after gynecological surgery: an effectiveness study in 410 women. Canadian Journal of Anesthesia 2002;49:1034‐9. [PUBMED: 12477673] - PubMed
Allen 1994 {published data only}
-
- Allen DL, Kitching AJ, Nagle C. P6 acupressure and nausea and vomiting after gynaecological surgery. Anaesthesia and Intensive Care 1994;22(6):691‐3. [PUBMED: 7892973] - PubMed
Amir 2007 {published data only}
-
- Amir SH, Bano S, Khan RM, Ahmed M, Zia F, Nasreen F. Electro‐stimulation at P6 for prevention of PONV. Journal of Anaesthesiology Clinical Pharmacology 2007;23:383‐86. [EMBASE: 2007618549]
Andrzejowski 1996 {published data only}
-
- Andrzejowski J, Woodward D. Semi‐permanent acupuncture needles in the prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting. Acupuncture in Medicine 1996;14:68‐70. [EMBASE: 1997049450]
Arnberger 2007 {published data only}
-
- Arnberger M, Stadelmann K, Alischer P, Ponert R, Melber A, Greif R, et al. Monitoring of neuromuscular blockade at the P6 acupuncture point reduces the incidence of postoperative nausea and vomiting. Anesthesiology 2007;107(6):903‐8. [PUBMED: 18043058] - PubMed
Barsoum 1990 {published data only}
Butkovic 2005 {published data only}
-
- Butkovic D, Toljan S, Matolic M, Kralik S, Radesić L. Comparison of laser acupuncture and metoclopramide in PONV prevention in children. Pediatric Anesthesia 2005;15(1):37‐40. [PUBMED: 15649161] - PubMed
Direkvand‐Moghadam 2013 {published data only}
Duggal 1998 {published data only}
-
- Duggal KN, Douglas MJ, Peter EA, Merrick PM. Acupressure for intrathecal narcotic‐induced nausea and vomiting after caesarean section. International Journal of Obstetric Anesthesia 1998;7:231‐6. [EMBASE: 1998371495] - PubMed
Dundee 1986 {published data only}
Dundee 1989 {published data only}
-
- Dundee JW, Fitzpatrick KTJ, Ghaly RG. Is there a role for acupuncture in the treatment of postoperative nausea and vomiting?. Anesthesiology 1987;67(3A):A165. [CENTRAL: CN‐00652348]
-
- Dundee JW, Ghaly RG, Bill KM, Chestnutt WN, Fitzpatrick KTJ, Lynas AGA. Effect of stimulation of the P6 antiemetic point on postoperative nausea and vomiting. British Journal of Anaesthesia 1989;63(5):612‐8. [PUBMED: 2605083] - PubMed
-
- Ghaly RG, Fitzpatrick KT, Dundee JW. Antiemetic studies with traditional Chinese acupuncture. A comparison of manual needling with electrical stimulation and commonly used antiemetics. Anaesthesia 1987;42(10):1108‐10. [PUBMED: 3688396] - PubMed
Ebrahim Soltani 2010 {published data only}
-
- Ebrahim Soltani A, Mohammadinasab H, Goudarzi M, Arbabi S, Mohtaram R, Afkham K, et al. Acupressure using ondansetron versus metoclopramide on reduction of postoperative nausea and vomiting after strabismus surgery. Archives of Iranian Medicine 2010;13(4):288‐93. [IRCT138807152556N1; PUBMED: 20597561] - PubMed
-
- Ebrahim Soltani AR, Mohammadinasab H, Goudarzi M, Arbabi S, Mohammadinasab A, Mohammadinasab F, et al. Comparing the efficacy of prophylactic p6 acupressure, ondansetron, metoclopramide and placebo in the prevention of vomiting and nausea after strabismus surgery. Acta Medica Iranica 2011;49(4):208‐12. [IRCT138807152556N1; PUBMED: 21713729] - PubMed
El‐Deeb 2011 {published data only}
-
- El‐Deeb AM, Ahmady MS. Effect of acupuncture on nausea and/or vomiting during and after cesarean section in comparison with ondansetron. Journal of Anesthesia 2011;25(5):698‐703. [PUBMED: 21761206] - PubMed
Ertas 2015 {published data only}
-
- Ertas G, Bengi Sener E, Kaya C, Ozkan F, Ustun YB, Koksal E. Effects of P6 acustimulation with the ReliefBand on postoperative nausea and vomiting in patients undergoing gynecological laparoscopy. Holistic Nursing Practice 2015;29(1):6‐12. [PUBMED: 25470475] - PubMed
Fassoulaki 1993 {published data only}
-
- Fassoulaki A, Papilas K, Sarantopoulos C, Zotou M. Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation reduces the incidence of vomiting after hysterectomy. Anesthesia and Analgesia 1993;76(5):1012‐4. [PUBMED: 8484499] - PubMed
Ferrara‐Love 1996 {published data only}
-
- Ferrara‐Love R, Sekeres L, Bircher NG. Nonpharmacological treatment of postoperative nausea. Journal of Perianesthesia Nursing 1996;11(6):378‐83. [PUBMED: 9069860] - PubMed
Frey 2009a {published data only}
-
- Frey UH, Scharmann P, Löhlein C, Peters J. P6 acustimulation effectively decreases postoperative nausea and vomiting in high‐risk patients. British Journal of Anaesthesia 2009;102(5):620‐5. [PUBMED: 19246457] - PubMed
Frey 2009b {published data only}
-
- Frey UH, Funk M, Löhlein C, Peters J. Effect of P6 acustimulation on postoperative nausea and vomiting in patients undergoing a laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica 2009;53(10):1341‐7. [PUBMED: 19681777] - PubMed
Gan 2004 {published data only}
-
- Gan TJ, Jiao KR, Zenn M, Georgiade G. A randomized controlled comparison of electro‐acupoint stimulation or ondansetron versus placebo for the prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting. Anesthesia and Analgesia 2004;99(4):1070‐5. [PUBMED: 15385352] - PubMed
Gieron 1993 {published data only}
-
- Gieron C, Wieland B, Laage D, Tolksdorf W. [Acupressure in the prophylaxis of postoperative nausea and vomiting]. Der Anaesthesist 1993;42(4):221‐6. [PUBMED: 8488993] - PubMed
Habib 2006 {published data only}
-
- Habib AS, Itchon‐Ramos N, Phillips‐Bute BG, Gan TJ, Duke Women's Anesthesia (DWA) Research Group. Transcutaneous acupoint electrical stimulation with the ReliefBand for the prevention of nausea and vomiting during and after Cesarean delivery under spinal anesthesia. Anesthesia and Analgesia 2006;102(2):581‐4. [PUBMED: 16428565] - PubMed
Harmon 1999 {published data only}
-
- Harmon D, Gardiner J, Harrison R, Kelly A. Acupressure and the prevention of nausea and vomiting after laparoscopy. British Journal of Anaesthesia 1999;82(3):387‐90. [PUBMED: 10434821] - PubMed
Harmon 2000 {published data only}
-
- Harmon D, Ryan M, Kelly A, Bowen M. Acupressure and prevention of nausea and vomiting during and after spinal anaesthesia for Caesarean section. British Journal of Anaesthesia 2000;84(4):463‐7. [PUBMED: 10823097] - PubMed
Ho 1990 {published data only}
-
- Ho RT, Jawan B, Fung ST, Cheung HK, Lee JH. Electro‐acupuncture and postoperative emesis. Anaesthesia 1990;45(4):327‐9. [PUBMED: 2140030] - PubMed
Ho 1996 {published data only}
-
- Ho CM, Hseu SS, Tsai SK, Lee TY. Effect of P6 acupressure on prevention of nausea and vomiting after epidural morphine for post‐Cesarean section pain relief. Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica 1996;40(3):372‐5. [PUBMED: 8721471] - PubMed
Iqbal 2012 {published data only}
-
- Iqbal U, Khan A, Sheikh F. Whether does acupressure (P6) prevent nausea and vomiting in patients undergoing laparoscopic surgery. Pakistan Journal of Medical and Health Sciences 2012;6(4):973‐5. [EMBASE: 2013071896]
Kim 2004 {published data only}
-
- Kim SI, Yoo IS, Park HN, Ok SY, Kim SC. Transcutaneous electrical stimulation of the P6 acupoint reduces postoperative nausea after minor breast surgery. Korean Journal of Anaesthesiology 2004;47:834‐9. [Identified from Kim KH et al. PLoS ONE 2012 review article]
Kim 2011 {published data only}
-
- Kim YH, Kim KS, Lee HJ, Shim JC, Yoon SW. The efficacy of several neuromuscular monitoring modes at the P6 acupuncture point in preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting. Anesthesia and Analgesia 2011;112(4):819‐23. [PUBMED: 21385974] - PubMed
Klein 2004 {published data only}
-
- Klein AA, Djaiani G, Karski J, Carroll J, Karkouti K, McCluskey S, et al. Acupressure wristbands for the prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting in adults undergoing cardiac surgery. Journal of Cardiothoracic and Vascular Anesthesia 2004;18(1):68‐71. [PUBMED: 14973803] - PubMed
Koo 2013 {published data only}
Lewis 1991 {published data only}
-
- Lewis IH, Pryn SJ, Reynolds PI, Pandit UA, Wilton NCT. Effect of P6 acupressure on postoperative vomiting in children undergoing outpatient strabismus correction. British Journal of Anaesthesia 1991;67(1):73‐8. [PUBMED: 1859764] - PubMed
Liu 2008 {published data only}
-
- Liu YY, Duan SE, Cai MX, Zou P, LY, Li YL. Evaluation of transcutaneous electroacupoint stimulation with the train‐of‐four mode for preventing nausea and vomiting after laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine 2008;14(2):94‐7. [PUBMED: 18679598] - PubMed
Majholm 2011 {published data only}
-
- Majholm B, Møller AM. Acupressure at acupoint P6 for prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting: a randomised clinical trial. European Journal of Anaesthesiology 2011;28(6):412‐9. [NCT00275483; PUBMED: 21544020] - PubMed
Misra 2005 {published data only}
-
- Misra MN, Pullani AJ, Mohamed ZU. Prevention of PONV by acustimulation with capsicum plaster is comparable to ondansetron after middle ear surgery. Canadian Journal of Anesthesia 2005;52(5):485‐9. [PUBMED: 15872126] - PubMed
Nilsson 2015 {published data only}
-
- Nilsson I, Karlsson A, Lindgren L, Bergenheim T, Koskinen LO, Nilsson U. The efficacy of P6 acupressure with Sea‐Band in reducing postoperative nausea and vomiting in patients undergoing craniotomy: a randomized, double‐blinded, placebo‐controlled study. Journal of Neurosurgical Anesthesiology 2015;27(1):42‐50. [NCT01617837; PUBMED: 24978062] - PubMed
Ravi 2010 {published data only}
-
- Ravi M, Babu G, Somasekharam N, Dinesh M, Asha N, Hamsa J. Comparative efficacy of acupuncture at p6 point with 0.2ml 50% dextrose and inj ondansetron 50ug kg‐1 iv for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting. Journal of Anaesthesiology Clinical Pharmacology 2010;26:237‐9. [EMBASE: 2010376316]
Rusy 2002 {published data only}
-
- Rusy LM, Hoffman GM, Weisman SJ. Electroacupuncture prophylaxis of postoperative nausea and vomiting following pediatric tonsillectomy with or without adenoidectomy. Anesthesiology 2002;96(2):300‐5. [PUBMED: 11818760] - PubMed
Sadighha 2008 {published data only}
Samad 2003 {published data only}
-
- Samad K, Afshan G, Kamal R. Effect of acupressure on postoperative nausea and vomiting in laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Journal of the Pakistan Medical Association 2003;53(2):68‐72. [PUBMED: 12705488] - PubMed
Schlager 1998 {published data only}
-
- Schlager A, Offer T, Baldissera I. Laser stimulation of acupuncture point P6 reduces postoperative vomiting in children undergoing strabismus surgery. British Journal of Anaesthesia 1998;81(4):529‐32. [PUBMED: 9924226] - PubMed
Schultz 2003 {published data only}
-
- Schultz AA, Andrews AL, Goran SF, Mathew T, Sturdevant N. Comparison of acupressure bands and droperidol for reducing post‐operative nausea and vomiting in gynecologic surgery patients. Applied Nursing Research 2003;16(4):256‐65. [PUBMED: 14608559] - PubMed
Sharma 2007 {published data only}
-
- Sharma S, Goswami U. Evaluation of acupuncture for anti‐emetic prophylaxis. Journal of Anaesthesiology Clinical Pharmacology 2007;23:401‐4. [EMBASE: 2007618554]
Shenkman 1999 {published data only}
-
- Shenkman Z, Holzman RS, Kim C, Ferrari LR, DiCanzio J, Highfield ES, et al. Acupressure‐acupuncture antiemetic prophylaxis in children undergoing tonsillectomy. Anesthesiology 1999;90(5):1311‐6. [PUBMED: 10319779] - PubMed
Streitberger 2004 {published data only}
-
- Schneider A, Löwe B, Streitberger K. Perception of bodily sensation as a predictor of treatment response to acupuncture for postoperative nausea and vomiting prophylaxis.. Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine 2005;11(1):119‐125. [PUBMED: 15750370] - PubMed
-
- Streitberger K, Diefenbacher M, Bauer A, Conradi R, Bardenheuer H, Martin E, et al. Acupuncture compared to placebo‐acupuncture for postoperative nausea and vomiting prophylaxis: a randomised placebo‐controlled patient and observer blind trial. Anaesthesia 2004;59(2):142‐9. [PUBMED: 14725517] - PubMed
Tavlan 1996 {published data only}
-
- Tavlan A, Baltaci B, Alptekin A, Ceyhan A, Unal N. A comparison of the effect of single dose ondansetron and P6 (neiguan) acupuncture point on postoperative nausea and vomiting for gynaecological laparoscopy. European Journal of Anaesthesiology. 1996; Vol. 13:164. [CN‐00258411]
Turgut 2007 {published data only}
-
- Turgut S, Ozalp G, Dikmen S, Savil S, Tuncel G, Kadiogullari N. Acupressure for postoperative nausea and vomiting in gynaecological patients receiving patient‐controlled analgesia. European Journal of Anaesthesiology 2007;24(1):87‐91. [PUBMED: 16895618] - PubMed
Wang 2002 {published data only}
-
- Wang SM, Kain ZN. P6 acupoint injections are as effective as droperidol in controlling early postoperative nausea and vomiting in children. Anesthesiology 2002;97(2):359‐66. [PUBMED: 12151925] - PubMed
Wang 2010 {published data only}
-
- Wang XQ, Yu JL, Du ZY, Xu R, Jiang CC, Gao X. Electroacupoint stimulation for postoperative nausea and vomiting in patients undergoing supratentorial craniotomy. Journal of Neurosurgical Anesthesiology 2010;22(2):128‐31. [PUBMED: 20308818] - PubMed
White 2002 {published data only}
-
- White PF, Issioui T, Hu J, Jones SB, Coleman JE, Waddle JP, et al. Comparative efficacy of acustimulation (ReliefBand) versus ondansetron (Zofran) in combination with droperidol for preventing nausea and vomiting. Anesthesiology 2002;97(5):1075‐81. [PUBMED: 12411789] - PubMed
White 2012 {published data only}
-
- White PF, Zhao M, Tang J, Wender RH, Yumul R, Sloninsky AV, et al. Use of a disposable acupressure device as part of a multimodal antiemetic strategy for reducing postoperative nausea and vomiting. Anesthesia and Analgesia 2012;115(1):31‐7. [NCT01317082; PUBMED: 22504214] - PubMed
Xu 2012 {published data only}
-
- Xu M, Zhou SJ, Jiang CC, Wu Y, Shi WL, Gu HH, et al. The effects of P6 electrical acustimulation on postoperative nausea and vomiting in patients after Infratentorial craniotomy. Journal of Neurosurgical Anesthesiology 2012;24(4):312‐6. [PUBMED: 22732720] - PubMed
Yang 1993 {published data only}
-
- Yang LC, Jawan B, Chen CN, Ho RT, Chang KA, Lee JH. Comparison of P6 acupoint injection with 50% glucose in water and intravenous droperidol for prevention of vomiting after gynecological laparoscopy. Acta Anaesthesiologica Scandinavica 1993;37(2):192‐4. [PUBMED: 8447210] - PubMed
Yentis 1992 {published data only}
-
- Yentis SM, Bissonnette B. Ineffectiveness of acupuncture and droperidol in preventing vomiting following strabismus repair in children. Canadian Journal of Anaesthesia 1992;39(2):151‐4. [PUBMED: 1544195] - PubMed
Zárate 2001 {published data only}
-
- Zárate E, Mingus M, White PF, Chiu JW, Scuderi P, Loskota W, et al. The use of transcutaneous acupoint electrical stimulation for preventing nausea and vomiting after laparoscopic surgery. Anesthesia and Analgesia 2001;92(3):629‐35. [PUBMED: 11226090] - PubMed
Zhu 2010 {published data only}
-
- Zhu HX, Xu YJ, Meng SF, Feng H, Liu Y, Su XJ. [Preventive effect of acupoint injection at neiguan (PC 6) on postoperative nausea and vomiting after laparoscopic gynecologic surgery]. Zhongguo zhen Jiu: Chinese Acupuncture and Moxibustion 2010;30(1):72‐4. [PUBMED: 20353120] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Agarwal 2005 {published data only}
-
- Agarwal A, Dhiraaj S, Tandon M, Singh PK, Singh U, Pawar S. Evaluation of capsaicin ointment at the Korean hand acupressure point K‐D2 for prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting. Anaesthesia 2005;60(12):1185‐8. [PUBMED: 16288616] - PubMed
Alkaissi 2005 {published data only}
-
- Alkaissi A, Ledin T, Odkvist LM, Kalman S. P6 acupressure increases tolerance to nauseogenic motion stimulation in women at high risk for PONV. Canadian Journal of Anesthesia 2005;52(7):703‐9. [PUBMED: 16103382] - PubMed
Al‐Sadi 1997 {published data only}
-
- Al‐Sadi M, Newman B, Julious SA. Acupuncture in the prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting. Anaesthesia 1997;52(7):658‐61. [PUBMED: 9244025] - PubMed
Cekmen 2007 {published data only}
-
- Cekmen N, Salman B, Keles Z, Aslan M, Akcabay M. Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation in the prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting after elective laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Journal of Clinical Anesthesia 2007;19(1):49‐52. [PUBMED: 17321927] - PubMed
Chen 2005 {published data only}
Coloma 2002 {published data only}
-
- Coloma M, White PF, Ogunnaike BO, Markowitz SD, Brown PM, Lee AQ, et al. Comparison of acustimulation and ondansetron for the treatment of established postoperative nausea and vomiting. Anesthesiology 2002;97(6):1387‐92. [PUBMED: 12459663] - PubMed
Dundee 1988 {published data only}
-
- Dundee JW, Milligan KR, McKay AC. Influence of intraoperative acupuncture and droperidol on postoperative emesis. British Journal of Anaesthesia 1988;61:116P‐7P.
Dundee 1991 {published data only}
-
- Dundee JW, Ghaly G. Local anesthesia blocks the antiemetic action of P6 acupuncture. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 1991;50(1):78‐80. [PUBMED: 1855355] - PubMed
El‐Bandrawy 2013 {published data only}
-
- El‐Bandrawy AM, Emara HM, Ghareeb HO. Transcutaneous electrical acupoint stimulation versus acupressure on postoperative nausea and vomiting after abdominal hysterectomy. British Journal of Medical Research 2013;3(4):2247‐55. [DOI: 10.9734/BJMMR/2013/4005] - DOI
El‐Rakshy 2009 {published data only}
-
- El‐Rakshy M, Clark SC, Thompson J, Thant M. Effect of intraoperative electroacupuncture on postoperative pain, analgesic requirements, nausea and sedation: a randomised controlled trial. Acupuncture in Medicine 2009;27(1):9‐12. [PUBMED: 19369187] - PubMed
Fan 1997 {published data only}
-
- Fan CF, Tanhui E, Joshi S, Trivedi S, Hong Y, Shevde K. Acupressure treatment for prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting. Anesthesia and Analgesia 1997;84(4):821‐5. [PUBMED: 9085965] - PubMed
Fry 1986 {published data only}
-
- Fry ENS. Acupressure and postoperative vomiting. Anaesthesia 1986;41(6):661‐2. [PUBMED: 3728942] - PubMed
Grube 2009 {published data only}
-
- Grube T, Uhlemann C, Weiss T, Meissner W. Influence of acupuncture on postoperative pain, nausea and vomiting after visceral surgery : a prospective, randomized comparative study of metamizole and standard treatment. Schmerz 2009;23(4):370‐6. [PUBMED: 19513760] - PubMed
Hirs 2013 {published data only}
-
- Hirs I, Lukic A, Fumic NN, Kekic M, Kotaran J. Acupressure and metoclopramide comparison in postoperative nausea and vomiting prevention on laparotomy patients. Acupuncture and Related Therapies 2013;1(4):42‐5. [EMBASE: 2013710528]
Ho 2006 {published data only}
-
- Ho CM, Tsai HJ, Chan KH, Tsai SK. P6 acupressure does not prevent emesis during spinal anesthesia for Cesarean delivery. Anesthesia and Analgesia 2006;102(3):900‐3. [PUBMED: 16492848] - PubMed
Jin 2013 {published data only}
-
- Jin W, Lu Y, Chen SD, Qin JL, Fang JQ, Wang JL. [Efficacy of preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting after thyroid tumor surgery by TAES at neiguan (P1): a clinical observation]. Chinese Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine 2013;33(9):1199‐202. [PUBMED: 24273973] - PubMed
Kabalak 2005 {published data only}
-
- Kabalak AA, Akcay M, Akcay F, Gogus N. Transcutaneous electrical acupoint stimulation versus ondansetron in the prevention of postoperative vomiting following pediatric tonsillectomy. Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine 2005;11(3):407‐13. [PUBMED: 15992223] - PubMed
Khan 2004 {published data only}
-
- Khan RM, Maroof M, Hakim S, Jain D, Ashraf M. Intraoperative stimulation of the P6 point controls postoperative nausea and vomiting following laparoscopic surgery. Canadian Journal of Anesthesia 2004;51(7):740‐1. [PUBMED: 15310647] - PubMed
Kim 2002 {published data only}
-
- Kim KS, Koo MS, Jeon JW, Park HS, Seung IS. Capsicum plaster at the Korean hand acupuncture point reduces postoperative nausea and vomiting after abdominal hysterectomy. Anesthesia and Analgesia 2002;95(4):1103‐7. [PUBMED: 12351304] - PubMed
Kim 2010 {published data only}
-
- Kim NC, Yoo JB, Cho MS, Shin EJ, Hahm TS. Effects of Nei‐Guan acupressure on nausea, vomiting and level of satisfaction for gynecological surgery patients who are using a patient‐controlled analgesia. Journal of Korean Academy of Nursing 2010;40:423‐32. [EMBASE: 20634633] - PubMed
Klaiman 2008 {published data only}
-
- Klaiman P, Sternfeld M, Deeb Z, Roth Y, Golan A, Ezri T, et al. Magnestic acupressure for management of postoperative nausea and vomiting: a preliminary study. Minerva Anestesiologica 2008;74(11):635‐42. [PUBMED: 18971892] - PubMed
Korinenko 2009 {published data only}
-
- Korinenko Y, Vincent A, Cutshall SM, Li Z, Sundt TM 3rd. Efficacy of acupuncture in prevention of postoperative nausea in cardiac surgery patients. Annals of Thoracic Surgery 2009;88(2):537‐42. [PUBMED: 19632409] - PubMed
Larson 2010 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Larson JD, Gutowski KA, Marcus BC, Rao VK, Avery PG, Stacey DH, et al. The effect of electroacustimulation on postoperative nausea, vomiting and pain in outpatient plastic surgery patients: a prospective randomized, blinded, clinical trial. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 2010;125(3):989‐94. [PUBMED: 20195124] - PubMed
Lee 2008 {published data only}
-
- Lee MY, Min HS. [Effects of the Nei‐Guan acupressure by wrist band on postoperative nausea and vomiting after middle ear surgery]. Taehan Kanho Hakhoe Chi 2008;38(4):503‐12. [PUBMED: 18753802] - PubMed
Lee 2013 {published data only}
-
- Lee S, Lee MS, Choi DH, Lee SK. Electroacupuncture on P6 prevents opioid‐induced nausea and vomiting after laparoscopic surgery. Chinese Journal of Integrated Medicine 2013;19(4):277‐81. [PUBMED: 23546631] - PubMed
Liodden 2011 {published data only}
-
- Liodden I, Howley M, Grimsgaard AS, Fønnebø VM, Borud EK, Alraek T, et al. Perioperative acupuncture and postoperative acupressure can prevent postoperative vomiting following paediatric tonsillectomy or adenoidectomy: a pragmatic randomised controlled trial. Acupuncture in Medicine 2011;29(1):9‐15. [NCT00965367; PUBMED: 21169634] - PubMed
Lu 2013 {published data only}
-
- Lü JQ, Feng RZ, Pan H, Li N. [A randomized controlled clinical trial for acupuncture stimulation of Neiguan (PC 6) to prevent postoperative nausea and vomiting]. Acupuncture Research 2013;38(3):245‐8. [PUBMED: 24006673] - PubMed
McConaghy 1996 {published data only}
-
- McConaghy P, Bland D, Swales H. Acupuncture in the management of postoperative nausea and vomiting in patients receiving morphine via a patient‐controlled analgesia system. Acupuncture in Medicine 1996;14(1):2‐5. [EMBASE: 1996251673]
McMillan 1994 {published data only}
-
- McMillan CM. Transcutaneous electrical stimulation of Neiguan antiemetic acupuncture point in controlling sickness following opioid analgesia in major orthopaedic surgery. Physiotherapy 1994;80:5‐9.
Ming 2002 {published data only}
-
- Ming JL, Kuo BI, Lin JG, Lin LC. The efficacy of acupressure to prevent nausea and vomiting in post‐operative patients. Journal of Advanced Nursing 2002;39(4):343‐51. [PUBMED: 12139646] - PubMed
Ng 2011 {published data only}
Norheim 2010 {published data only}
-
- Norheim AJ, Liodden I, Howley M. Implementation of acupuncture and acupressure under surgical procedures in children: a pilot study. Acupuncture in Medicine 2010;28(2):71‐3. [PUBMED: 20458123] - PubMed
Noroozinia 2013 {published data only}
-
- Noroozinia H, Mahoori A, Hasani E, Gerami‐Fahim M, Sepehrvand N. The effect of acupressure on nausea and vomiting after cesarean section under spinal anesthesia. Acta Medica Iranica 2013;51(3):163‐7. [PUBMED: 23605600] - PubMed
Ouyang 2009 {published data only}
-
- Ouyang MW, Qin ZS, Lin CS, Gu MN. [Prophylactic effect of acupuncture on nausea and vomiting after laparoscopic operation]. Zhongguo zhen Jiu: Chinese Acupuncture and Moxibustion 2009;29(11):915‐8. [PUBMED: 19994693] - PubMed
Phillips 1994 {published data only}
-
- Phillips K, Gill L. The use of simple acupressure bands reduces post‐operative nausea. Complementary Therapies in Medicine 1994;2:158‐60.
Schwager 1996 {published data only}
-
- Schwager KL, Baines DB, Meyer RJ. Acupuncture and postoperative vomiting in day‐stay paediatric patients. Anaesthesia and Intensive Care 1996;24(6):674‐7. [PUBMED: 8971315] - PubMed
Shyr 1990 {published data only}
-
- Shyr MH, Hsu JC, Wu YW, Hui YL, Tan PPC. [P6 acupoint injection reduced postoperative nausea and vomiting]. Ma Tsui Hsueh Tsa Chi Anaesthesiologica Sinica 1990;28(3):357‐60. [PUBMED: 2277579] - PubMed
Sinha 2011 {published data only}
-
- Sinha A, Paech MJ, Thew ME, Rhodes M, Luscombe K, Nathan E. A randomised, double‐blinded, placebo‐controlled study of acupressure wristbands for the prevention of nausea and vomiting during labour and delivery. International Journal of Obstetric Anesthesia 2011;20(2):110‐7. [PUBMED: 21194921] - PubMed
Somri 2001 {published data only}
-
- Somri M, Vaida SJ, Sabo E, Yassain G, Gankin I, Gaitini LA. Acupuncture versus ondansetron in the prevention of postoperative vomiting. Anaesthesia 2001;56(10):927‐32. [PUBMED: 11576093] - PubMed
Stein 1997 {published data only}
-
- Stein DJ, Birnbach DJ, Danzer BI, Kuroda MM, Grunebaum A, Thys DM. Acupressure versus intravenous metoclopramide to prevent nausea and vomiting during spinal anesthesia for cesarean section. Anesthesia and Analgesia 1997;84(2):342‐5. [PUBMED: 9024025] - PubMed
Tang 2013 {published data only}
-
- Tang W, Ma W, Fu GQ, Yuan L, Shen WD. Impacts of electroacupuncture at different frequencies on the postoperative nausea and vomiting of patients with laparoscopic surgery. Zhonggui zhen Jiu: Chinese Acupuncture and Moxibustion 2013;33(2):159‐62. [PUBMED: 23620949] - PubMed
Wang 2014 {published data only}
-
- Wang H, Xie Y, Zhang Q, Xu N, Zhong H, Dong H, et al. Transcutaneous electric acupoint stimulation reduces intra‐operative remifentanil consumption and alleviates postoperative side‐effects in patients undergoing sinusotomy: a prospective, randomized, placebo‐controlled trial. British Journal of Anaesthesia 2014;112(6):1075‐82. [PUBMED: 24576720] - PubMed
Weightman 1987 {published data only}
White 2005 {published data only}
-
- White PF, Hamza MA, Recart A, Coleman JE, Macaluso AR, Cox L, Jaffer O, Song D, Rohrich R. Optimal timing of acustimulation for antiemetic prophylaxis as an adjunct to ondansetron in patients undergoing plastic surgery. Anesthesia and Analgesia 2005;100(2):367‐72. [PUBMED: 15673859] - PubMed
Windle 2001 {published data only}
-
- Windle PE, Borromeo A, Robles H, Ilacio‐Uy V. The effects of acupressure on the incidence of postoperative nausea and vomiting in postsurgical patients. Journal of Perianesthesia Nursing 2001;16(3):158‐62. [PUBMED: 11395836] - PubMed
Yeh 2010 {published data only}
-
- Yeh ML, Chung YC, Chen KM, Tsou MY, Chen HH. Acupoint electrical stimulation reduces acute postoperative pain in surgical patients with patient‐controlled analgesia: a randomized controlled study. Alternative Therapies in Health and Medicine 2010;16:10‐18. [EMBASE: 21280458] - PubMed
Yentis 1991 {published data only}
-
- Yentis SM, Bissonnette B. P6 acupuncture and postoperative vomiting after tonsillectomy in children. British Journal of Anaesthesia 1991;67(6):779‐80. [PUBMED: 1768550] - PubMed
Yentis 1998 {published data only}
-
- Yentis SM, Vashisht S. The effect of timing of P6 acupuncture on post‐operative vomiting following major gynaecological surgery. Acupuncture in Medicine 1998;16:10‐13.
Zheng 2008 {published data only}
-
- Zheng LH, Sun H, Wang GN, Liang J, Wu HX. Effect of transcutaneous electrical acupoint stimulation on nausea and vomiting induced by patient controlled intravenous analgesia with tramadol. Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine 2008;14(1):61‐4. [PUBMED: 18219451] - PubMed
References to ongoing studies
Cooke 2014 {published data only}
Additional references
Afshari 2015
-
- Afshari A, Wetterslev J. When may systematic reviews and meta‐analyses be considered reliable?. European Journal of Anaesthesiology 2015;32(2):85‐7. [PUBMED: 25536187] - PubMed
Altman 1998
Altman 2003
Apfel 1999
-
- Apfel CC, Läärä E, Koivuranta M, Greim CA, Roewer N. A simplified risk score for predicting postoperative nausea and vomiting: conclusions from cross‐validations between two centers. Anesthesiology 1999;91(3):693‐700. [PUBMED: 10485781] - PubMed
Apfel 2007
-
- Apfel CC, Kranke P, Piper S, Rüsch D, Kerger H, Steinfath M, et al. Nausea and vomiting in the postoperative phase. Expert‐ and evidence‐based recommendations for prophylaxis and therapy [Übelkeit und erbrechen in der postoperativen phase]. Der Anaesthesist 2007;56(11):1170‐80. [PUBMED: 17726590] - PubMed
Carlisle 2006
Cheong 2013
Duval 2000
-
- Duval S, Tweedie R. Trim and fill: a simple funnel‐plot‐based method of testing and adjusting for publication bias in meta‐analysis. Biometrics 2000;56(2):455‐63. [PUBMED: 10877304] - PubMed
Gan 2014
-
- Gan TJ, Diemunsch P, Habib AS, Kovac A, Kranke P, Meyer TA, et al. Consensus guidelines for the management of postoperative nausea and vomiting. Anesthesia and Analgesia 2014;118(1):85‐113. [PUBMED: 24356162] - PubMed
Gin 1994
-
- Gin T. Recent advances in the understanding and management of postoperative nausea and vomiting. Annals of Academic Medicine of Singapore 1994;23(6 Suppl):114‐9. [PUBMED: 7710220] - PubMed
Guyatt 2011
-
- Guyatt G, Oxman AD, Akl EA, Kunz R, Vist G, Brozek J, et al. GRADE guidelines: 1. Introduction‐GRADE evidence profiles and summary of findings tables.. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2011;64(4):383‐94. [PUBMED: 21195583 ] - PubMed
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from www.cochrane‐handbook.org.
Kim 2012
Lee 2006
-
- Lee A, Copas JB, Henmi M, Gin T, Chung RCK. Publication bias affected the estimate of postoperative nausea in an acupoint stimulation systematic review. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2006;59(9):980‐3. [PUBMED: 16895822] - PubMed
Mann 1987
-
- Mann F. Textbook of Acupuncture. London: William Heinemann Medical Books, 1987.
McAuley 2000
-
- McAuley L, Pham B, Tugwell P, Moher D. Does the inclusion of grey literature influence estimates of intervention effectiveness reported in meta‐analyses?. Lancet 2000;356(9237):1228‐31. [PUBMED: 11072941] - PubMed
Mosteller 1996
-
- Mosteller F, Colditz GA. Understanding research synthesis (meta‐analysis). Annual Review of Public Health 1996;17:1‐23. [PUBMED: 8724213] - PubMed
Peters 2008
-
- Peters JL, Sutton AJ, Jones DR, Abrams KR, Rushton L. Contour‐enhanced meta‐analysis funnel plots help distinguish publication bias from other causes of asymmetry. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2008;61(10):991‐6. [PUBMED: 18538991] - PubMed
Petitti 1994
-
- Petitti DB. Meta‐analysis, Decision Analysis and Cost‐Effectiveness Analysis: Methods for Quantitative Synthesis in Medicine. New York: Oxford University Press, 1994.
Sadhasivam 1999
-
- Sadhasivam S, Saxena A, Kathirvel S, Kannan TR, Trikha A, Mohan V. The safety and efficacy of prophylactic ondansetron in patients undergoing modified radical mastectomy. Anesthesia and Analgesia 1999;89(6):1340‐5. [PUBMED: 10589605] - PubMed
Smeeth 1999
Streitberger 2011
-
- Streitberger K, Kranke P. Evidence for the efficacy of acupressure for preventing post‐operative nausea and vomiting: an ongoing debate. European Journal of Anaesthesiology 2011;28(6):396‐8. [PUBMED: 21088590] - PubMed
Tang 1999
Thorlund 2011
-
- Thorlund K, Engstrøm J, Wetterslev J, Brok J, Imberger G, Gluud C. User Manual for Trial Sequential Analysis (TSA).. Copenhagen, Denmark: Copenhagen Trial Unit, Centre for Clinical Intervention Research, 2011. [www.ctu.dk/tsa]
Van Driel 2009
-
- Driel ML, Sutter A, Maeseneer J, Christiaens T. Searching for unpublished trials in Cochrane reviews may not be worth the effort. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 2009;62(8):838‐44. [PUBMED: 19128939] - PubMed
Vickers 1996
Watcha 1992
-
- Watcha MF, White PF. Postoperative nausea and vomiting: its etiology, treatment and prevention. Anesthesiology 1992;77(1):162‐84. [PUBMED: 1609990] - PubMed
White 1999
-
- White PF, Watcha MF. Has the use of meta‐analysis enhanced our understanding of therapies for postoperative nausea and vomiting?. Anesthesia and Analgesia 1999;88(6):1200‐2. [PUBMED: 10357318] - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Lee 1999
-
- Lee A, Done ML. The use of nonpharmacologic techniques to prevent postoperative nausea and vomiting: a meta‐analysis. Anesthesia and Analgesia 1999;88(6):1362‐9. [PUBMED: 10357346] - PubMed
Lee 2001
-
- Lee A, Done ML. Acupoint P6 stimulaton for preventing postoperative nausea and vomiting. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2001, Issue 4. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD003281] - DOI
Lee 2004
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

