Extracellular rigidity sensing by talin isoform-specific mechanical linkages
- PMID: 26523364
- PMCID: PMC4662888
- DOI: 10.1038/ncb3268
Extracellular rigidity sensing by talin isoform-specific mechanical linkages
Abstract
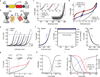
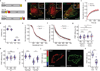
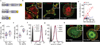
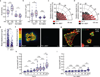
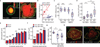
The ability of cells to adhere and sense differences in tissue stiffness is crucial for organ development and function. The central mechanisms by which adherent cells detect extracellular matrix compliance, however, are still unknown. Using two single-molecule-calibrated biosensors that allow the analysis of a previously inaccessible but physiologically highly relevant force regime in cells, we demonstrate that the integrin activator talin establishes mechanical linkages following cell adhesion, which are indispensable for cells to probe tissue stiffness. Talin linkages are exposed to a range of piconewton forces and bear, on average, 7-10 pN during cell adhesion depending on their association with F-actin and vinculin. Disruption of talin's mechanical engagement does not impair integrin activation and initial cell adhesion but prevents focal adhesion reinforcement and thus extracellular rigidity sensing. Intriguingly, talin mechanics are isoform specific so that expression of either talin-1 or talin-2 modulates extracellular rigidity sensing.
Figures
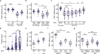

Comment in
-
Sensing some tension.Nat Methods. 2016 Jan;13(1):17. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3726. Nat Methods. 2016. PMID: 27110628 No abstract available.
References
-
- Heisenberg CP, Bellaiche Y. Forces in tissue morphogenesis and patterning. Cell. 2013;153:948–962. - PubMed
-
- Franze K, Janmey PA, Guck J. Mechanics in neuronal development and repair. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2013;15:227–251. - PubMed
-
- Ingber DE. Mechanobiology and diseases of mechanotransduction. Ann. Med. 2003;35:564–577. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

