De Novo Donor-Specific HLA Antibody Formation in Two Patients With Crigler-Najjar Syndrome Type I Following Human Hepatocyte Transplantation With Partial Hepatectomy Preconditioning
- PMID: 26523372
- PMCID: PMC5061095
- DOI: 10.1111/ajt.13487
De Novo Donor-Specific HLA Antibody Formation in Two Patients With Crigler-Najjar Syndrome Type I Following Human Hepatocyte Transplantation With Partial Hepatectomy Preconditioning
Abstract
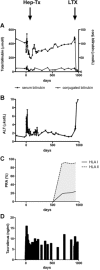
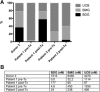
Clinical hepatocyte transplantation is hampered by low engraftment rates and gradual loss of function resulting in incomplete correction of the underlying disease. Preconditioning with partial hepatectomy improves engraftment in animal studies. Our aim was to study safety and efficacy of partial hepatectomy preconditioning in clinical hepatocyte transplantation. Two patients with Crigler-Najjar syndrome type I underwent liver resection followed by hepatocyte transplantation. A transient increase of hepatocyte growth factor was seen, suggesting that this procedure provides a regenerative stimulus. Serum bilirubin was decreased by 50%, and presence of bilirubin glucuronides in bile confirmed graft function in both cases; however, graft function was lost due to discontinuation of immunosuppressive therapy in one patient. In the other patient, serum bilirubin gradually increased to pretransplant concentrations after ≈600 days. In both cases, loss of graft function was temporally associated with emergence of human leukocyte antigen donor-specific antibodies (DSAs). In conclusion, partial hepatectomy in combination with hepatocyte transplantation was safe and induced a robust release of hepatocyte growth factor, but its efficacy on hepatocyte engraftment needs to be evaluated with additional studies. To our knowledge, this study provides the first description of de novo DSAs after hepatocyte transplantation associated with graft loss.
Keywords: cellular transplantation (non-islet); immune regulation; liver (native) function/dysfunction; liver disease: congenital; liver transplantation/hepatology; regenerative medicine; translational research/science.
© Copyright 2015 The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons.
Figures



Comment in
-
Hepatocyte Transplantation and Humoral Alloimmunity.Am J Transplant. 2016 Jun;16(6):1940. doi: 10.1111/ajt.13662. Epub 2016 Feb 22. Am J Transplant. 2016. PMID: 26696593 No abstract available.
References
-
- Strauss KA, Robinson DL, Vreman HJ, Puffenberger EG, Hart G, Morton DH. Management of hyperbilirubinemia and prevention of kernicterus in 20 patients with Crigler‐Najjar disease. Eur J Pediatr 2006; 165: 306–319. - PubMed
-
- Jorns C, Ellis EC, Nowak G, et al. Hepatocyte transplantation for inherited metabolic diseases of the liver. J Intern Med 2012; 272: 201–223. - PubMed
-
- Gupta S, Johnstone R, Darby H, Selden C, Price Y, Hodgson HJ. Transplanted isolated hepatocytes: Effect of partial hepatectomy on proliferation of long‐term syngeneic implants in rat spleen. Pathology 1987; 19: 28–30. - PubMed
-
- Taner T, Stegall MD, Heimbach JK. Antibody‐mediated rejection in liver transplantation: Current controversies and future directions. Liver Transpl 2014; 20: 514–527. - PubMed
-
- Campbell PM, Senior PA, Salam A, et al. High risk of sensitization after failed islet transplantation. Am J Transplant 2007; 7: 2311–2317. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

