Organ iron accumulation in chronically transfused children with sickle cell anaemia: baseline results from the TWiTCH trial
- PMID: 26523836
- PMCID: PMC4715688
- DOI: 10.1111/bjh.13791
Organ iron accumulation in chronically transfused children with sickle cell anaemia: baseline results from the TWiTCH trial
Abstract
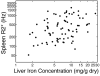
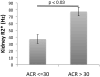
Transcranial Doppler (TCD) With Transfusions Changing to Hydroxyurea (TWiTCH) trial is a randomized, open-label comparison of hydroxycarbamide (also termed hydroxyurea) versus continued chronic transfusion therapy for primary stroke prevention in patients with sickle cell anaemia (SCA) and abnormal TCD. Severity and location of iron overload is an important secondary outcome measure. We report the baseline findings of abdominal organ iron burden in 121 participants. At enrollment, patients were young (9·8 ± 2·9 years), predominantly female (60:40), and previously treated with transfusions (4·1 ± 2·4 years) and iron chelation (3·1 ± 2·1 years). Liver iron concentration (LIC; 9·0 ± 6·6 mg/g dry weight) and serum ferritin were moderately elevated (2696 ± 1678 μg/l), but transferrin was incompletely saturated (47·2 ± 23·6%). Spleen R2* was 509 ± 399 Hz (splenic iron ~13·9 mg/g) and correlated with LIC (r(2) = 0·14, P = 0·0008). Pancreas R2* was increased in 38·3% of patients but not to levels associated with endocrine toxicity. Kidney R2* was increased in 80·7% of patients; renal iron correlated with markers of intravascular haemolysis and was elevated in patients with increased urine albumin-creatinine ratios. Extra-hepatic iron deposition is common among children with SCA who receive chronic transfusions, and could potentiate oxidative stress caused by reperfusion injury and decellularized haemoglobin.
Keywords: MRI; iron overload; sickle cell anaemia; sickle cell radiology; transfusions.
© 2015 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures

References
-
- Adams RJ, Brambilla D. Discontinuing prophylactic transfusions used to prevent stroke in sickle cell disease. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:2769–2778. - PubMed
-
- Armstrong-Wells J, Grimes B, Sidney S, Kronish D, Shiboski SC, Adams RJ, Fullerton HJ. Utilization of TCD screening for primary stroke prevention in children with sickle cell disease. Neurology. 2009;72:1316–1321. - PubMed
-
- Bernaudin F, Verlhac S, Arnaud C, Kamdem A, Chevret S, Hau I, Coic L, Leveille E, Lemarchand E, Lesprit E, Abadie I, Medejel N, Madhi F, Lemerle S, Biscardi S, Bardakdjian J, Galacteros F, Torres M, Kuentz M, Ferry C, Socie G, Reinert P, Delacourt C. Impact of early transcranial Doppler screening and intensive therapy on cerebral vasculopathy outcome in a newborn sickle cell anemia cohort. Blood. 2011;117:1130–1140. quiz 1436. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

