Regulatory T cells in cardiovascular diseases
- PMID: 26525543
- PMCID: PMC11849084
- DOI: 10.1038/nrcardio.2015.169
Regulatory T cells in cardiovascular diseases
Abstract
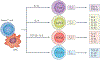
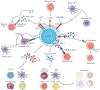
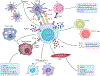
Inflammation is essential in the initial development and progression of many cardiovascular diseases involving innate and adaptive immune responses. The role of CD4(+)CD25(+)FOXP3(+) regulatory T (TREG) cells in the modulation of inflammation and immunity has received increasing attention. Given the important role of TREG cells in the induction and maintenance of immune homeostasis and tolerance, dysregulation in the generation or function of TREG cells can trigger abnormal immune responses and lead to pathology. A wealth of evidence from experimental and clinical studies has indicated that TREG cells might have an important role in protecting against cardiovascular disease, in particular atherosclerosis and abdominal aortic aneurysm. In this Review, we provide an overview of the roles of TREG cells in the pathogenesis of a number of cardiovascular diseases, including atherosclerosis, hypertension, ischaemic stroke, abdominal aortic aneurysm, Kawasaki disease, pulmonary arterial hypertension, myocardial infarction and remodelling, postischaemic neovascularization, myocarditis and dilated cardiomyopathy, and heart failure. Although the exact molecular mechanisms underlying the cardioprotective effects of TREG cells are still to be elucidated, targeted therapies with TREG cells might provide a promising and novel future approach to the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular diseases.
Figures

References
-
- Fontenot JD, Gavin MA & Rudensky AY Foxp3 programs the development and function of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. Nat. Immunol 4, 330–336 (2003). - PubMed
-
- Sakaguchi S. Naturally arising Foxp3-expressing CD25+CD4+ regulatory T cells in immunological tolerance to self and non-self. Nat. Immunol 6, 345–352 (2005). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

