PTEN is required to maintain luminal epithelial homeostasis and integrity in the adult mammary gland
- PMID: 26526198
- PMCID: PMC4688181
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2015.10.023
PTEN is required to maintain luminal epithelial homeostasis and integrity in the adult mammary gland
Abstract
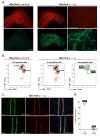
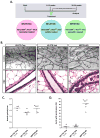
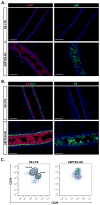
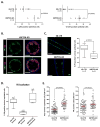
In the mammary gland, PTEN loss in luminal and basal epithelial cells results in differentiation defects and enhanced proliferation, leading to the formation of tumors with basal epithelial characteristics. In breast cancer, PTEN loss is associated with a hormone receptor-negative, basal-like subtype that is thought to originate in a luminal epithelial cell. Here, we show that luminal-specific PTEN loss results in distinct effects on epithelial homeostasis and mammary tumor formation. Luminal PTEN loss increased proliferation of hormone receptor-negative cells, thereby decreasing the percentage of hormone receptor-positive cells. Moreover, luminal PTEN loss led to misoriented cell divisions and mislocalization of cells to the intraluminal space of mammary ducts. Despite their elevated levels of activated AKT, Pten-null intraluminal cells showed increased levels of apoptosis. One year after Pten deletion, the ducts had cleared and no palpable mammary tumors were detected. These data establish PTEN as a critical regulator of luminal epithelial homeostasis and integrity in the adult mammary gland, and further show that luminal PTEN loss alone is not sufficient to promote the progression of mammary tumorigenesis.
Keywords: Epithelial; Homeostasis; Mammary; PTEN.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
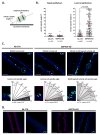
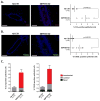
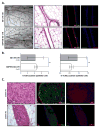
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- CA016303-39/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA016303/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30AI036211/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HD083092/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- S10RR024574/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U54HD083092/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- P30CA125123/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K99 NS087095/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA125123/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI036211/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- NS087095/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR024574/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA016303/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R00 NS087095/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

