Coordination of m(6)A mRNA Methylation and Gene Transcription by ZFP217 Regulates Pluripotency and Reprogramming
- PMID: 26526723
- PMCID: PMC4671830
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2015.09.005
Coordination of m(6)A mRNA Methylation and Gene Transcription by ZFP217 Regulates Pluripotency and Reprogramming
Abstract
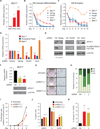
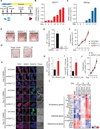
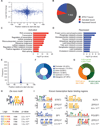
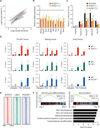
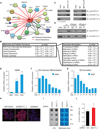
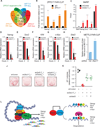
Epigenetic and epitranscriptomic networks have important functions in maintaining the pluripotency of embryonic stem cells (ESCs) and somatic cell reprogramming. However, the mechanisms integrating the actions of these distinct networks are only partially understood. Here we show that the chromatin-associated zinc finger protein 217 (ZFP217) coordinates epigenetic and epitranscriptomic regulation. ZFP217 interacts with several epigenetic regulators, activates the transcription of key pluripotency genes, and modulates N6-methyladenosine (m(6)A) deposition on their transcripts by sequestering the enzyme m(6)A methyltransferase-like 3 (METTL3). Consistently, Zfp217 depletion compromises ESC self-renewal and somatic cell reprogramming, globally increases m(6)A RNA levels, and enhances m(6)A modification of the Nanog, Sox2, Klf4, and c-Myc mRNAs, promoting their degradation. ZFP217 binds its own target gene mRNAs, which are also METTL3 associated, and is enriched at promoters of m(6)A-modified transcripts. Collectively, these findings shed light on how a transcription factor can tightly couple gene transcription to m(6)A RNA modification to ensure ESC identity.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Boiani M, Scholer HR. Regulatory networks in embryo-derived pluripotent stem cells. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2005;6:872–884. - PubMed
-
- Bujnicki JM, Feder M, Radlinska M, Blumenthal RM. Structure prediction and phylogenetic analysis of a functionally diverse family of proteins homologous to the MT-A70 subunit of the human mRNA:m(6)A methyltransferase. J Mol Evol. 2002;55:431–444. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- CA154903/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM112763/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL103967/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM095942/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA154809/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HL103967/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R24 CA088325/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DA028776/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- GM089778/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- RC1 DA028776/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 NS061777/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM089778/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01-GM095942/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

