The interaction effects of aerobic exercise training and vitamin D supplementation on plasma lipid profiles and insulin resistance in ovariectomized rats
- PMID: 26526941
- PMCID: PMC4624118
- DOI: 10.5717/jenb.2015.15070703
The interaction effects of aerobic exercise training and vitamin D supplementation on plasma lipid profiles and insulin resistance in ovariectomized rats
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to determine the interaction effects of aerobic exercise training and vitamin D supplementation on indices of obesity and plasma lipid profiles in ovariectomized (OVX) rats.
Methods: Forty female Wistar rats were divided into 5 groups: aerobic training (3 days/week for 8 weeks; AT; n = 8), aerobic training and vitamin D supplementation (OVX + AT + Vit D; n = 8), vitamin D supplementation (OVX + Vit D; n = 8), ovariectomized control (OVX + C, n = 8) and SHAM (n = 8). After blood sampling, visceral fat was taken from the abdominal cavity and weighed immediately. Data was statistically analyzed by One-way ANOVA and Repeated measure ANOVA tests with a 0.05 significance level.
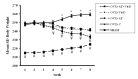
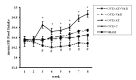
Results: Body weight, visceral fat, BMI and food intake decreased significantly in OVX + AT + Vit D (P < 0.001); whereas these variables increased significantly in OVX + C (P < 0.001) and SHAM (P < 0.023) groups. At the end of two-months of follow-up, we observed significant differences in TC, TG, HDL-C, LDL-C, glucose, insulin, and HOMA-IR in all groups.
Conclusion: It seems that aerobic training with vitamin D, due to the involvement of muscle mass and exposure to dynamic pressure on the bones and muscles, increased energy expenditure, stimulated insulin exudation and glucose homeostasis, decreased insulin resistance and improved the lipid profile in ovariectomized rats.
Keywords: Aerobic Training; Food Intake; Postmenopausal Women; Visceral Fat; Vitamin D; plasma lipid profiles and insulin resistance.
Figures
References
-
- Cooke PS, Naaz A. Role of estrogens in adipocyte development and function. Experimental biology and medicine. 2004;229:1127–35. - PubMed
-
- Wajchenberg BL. Subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue: their relation to the metabolic syndrome. Endocrine reviews. 2000;21:697–738. - PubMed
-
- Ainslie D, Morris M, Wittert G, Turnbull H, Proietto J, Thorburn A. Estrogen deficiency causes central leptin insensitivity and increased hypothalamic neuropeptide Y. International journal of obesity and related metabolic disorders: journal of the International Association for the Study of Obesity. 2001;25:1680–8. - PubMed
-
- Roth SM, Zmuda JM, Cauley JA, Shea PR, Ferrell RE. Vitamin D receptor genotype is associated with fat-free mass and sarcopenia in elderly men. The Journals of Gerontology Series A: Biological Sciences and Medical Sciences. 2004;59:10–5. - PubMed
-
- Gambacciani M, Ciaponi M, Cappagli B, Piaggesi L, De Simone L, Orlandi R, et al. Body weight, body fat distribution, and hormonal replacement therapy in early postmenopausal women. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. 1997;82:414–7. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

