Bringing CLARITY to the human brain: visualization of Lewy pathology in three dimensions
- PMID: 26526972
- PMCID: PMC5053282
- DOI: 10.1111/nan.12293
Bringing CLARITY to the human brain: visualization of Lewy pathology in three dimensions
Abstract
Aims: CLARITY is a novel technique which enables three-dimensional visualization of immunostained tissue for the study of circuitry and spatial interactions between cells and molecules in the brain. In this study, we aimed to compare methodological differences in the application of CLARITY between rodent and large human post mortem brain samples. In addition, we aimed to investigate if this technique could be used to visualize Lewy pathology in a post mortem Parkinson's brain.
Methods: Rodent and human brain samples were clarified and immunostained using the passive version of the CLARITY technique. Samples were then immersed in different refractive index matching media before mounting and visualizing under a confocal microscope.
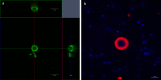
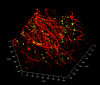
Results: We found that tissue clearing speed using passive CLARITY differs according to species (human vs. rodents), brain region and degree of fixation (fresh vs. formalin-fixed tissues). Furthermore, there were advantages to using specific refractive index matching media. We have applied this technique and have successfully visualized Lewy body inclusions in three dimensions within the nucleus basalis of Meynert, and the spatial relationship between monoaminergic fibres and Lewy pathologies among nigrostriatal fibres in the midbrain without the need for physical serial sectioning of brain tissue.
Conclusions: The effective use of CLARITY on large samples of human tissue opens up many potential avenues for detailed pathological and morphological studies.
Keywords: CLARITY; Lewy body pathology; human post mortem brain; three-dimensional visualization; tissue clearing.
© 2015 The Authors. Neuropathology and Applied Neurobiology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of British Neuropathological Society.
Figures




Similar articles
-
TIGAR inclusion pathology is specific for Lewy body diseases.Brain Res. 2019 Mar 1;1706:218-223. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2018.09.032. Epub 2018 Sep 26. Brain Res. 2019. PMID: 30267647
-
3D imaging in the postmortem human brain with CLARITY and CUBIC.Handb Clin Neurol. 2018;150:303-317. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-444-63639-3.00021-9. Handb Clin Neurol. 2018. PMID: 29496149
-
α-Synuclein and Lewy pathology in Parkinson's disease.Curr Opin Neurol. 2015 Aug;28(4):375-81. doi: 10.1097/WCO.0000000000000215. Curr Opin Neurol. 2015. PMID: 26110807 Review.
-
Three-layered structure shared between Lewy bodies and lewy neurites-three-dimensional reconstruction of triple-labeled sections.Brain Pathol. 2008 Jul;18(3):415-22. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2008.00140.x. Epub 2008 Apr 2. Brain Pathol. 2008. PMID: 18394008 Free PMC article.
-
Review: Clinical, neuropathological and genetic features of Lewy body dementias.Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2019 Dec;45(7):635-654. doi: 10.1111/nan.12554. Epub 2019 May 20. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 30977926 Review.
Cited by
-
Developing 3D microscopy with CLARITY on human brain tissue: Towards a tool for informing and validating MRI-based histology.Neuroimage. 2018 Nov 15;182:417-428. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2017.11.060. Epub 2017 Nov 28. Neuroimage. 2018. PMID: 29196268 Free PMC article.
-
Three dimensional evaluation of cerebrovascular density and branching in chronic traumatic encephalopathy.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2023 Jul 25;11(1):123. doi: 10.1186/s40478-023-01612-y. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2023. PMID: 37491342 Free PMC article.
-
Optimizing tissue clearing and imaging methods for human brain tissue.J Int Med Res. 2021 Mar;49(3):3000605211001729. doi: 10.1177/03000605211001729. J Int Med Res. 2021. PMID: 33771067 Free PMC article.
-
A Clearing Technique to Enhance Endogenous Fluorophores in Skin and Soft Tissue.Sci Rep. 2019 Oct 31;9(1):15791. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-50359-x. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31673001 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping causal pathways from genetics to neuropsychiatric disorders using genome-wide imaging genetics: Current status and future directions.Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2019 Jul;73(7):357-369. doi: 10.1111/pcn.12839. Epub 2019 May 21. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 30864184 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Conchello J‐A, Lichtman JW. Optical sectioning microscopy. Nat Methods 2005; 2: 920–931. - PubMed
-
- Spalteholz W. Über das Durchsightigmachen von menschlichen und tierischen Präparaten: nebst Anhang, Über Knochenfärbung. Leipzig: Verlag von S. Hirzel, 1911.
-
- Duvernoy HM. The human hippocampus: functional anatomy, vascularization and serial sections with MRI. 3rd edn Berlin: Springer‐Verlag, 2005.
-
- Dodt H‐U, Leischner U, Schierloh A, Jährling N, Mauch CP, Deininger K, Deussing JM, Eder M, Zieglgänsberger W, Becker K. Ultramicroscopy: three‐dimensional visualization of neuronal networks in the whole mouse brain. Nat Methods 2007; 4: 331–336. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

