Structural Basis of Ribosomal S6 Kinase 1 (RSK1) Inhibition by S100B Protein: MODULATION OF THE EXTRACELLULAR SIGNAL-REGULATED KINASE (ERK) SIGNALING CASCADE IN A CALCIUM-DEPENDENT WAY
- PMID: 26527685
- PMCID: PMC4697148
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M115.684928
Structural Basis of Ribosomal S6 Kinase 1 (RSK1) Inhibition by S100B Protein: MODULATION OF THE EXTRACELLULAR SIGNAL-REGULATED KINASE (ERK) SIGNALING CASCADE IN A CALCIUM-DEPENDENT WAY
Abstract
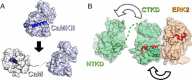
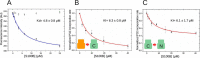
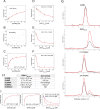
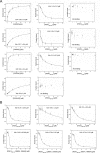
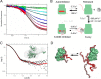
Mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPK) promote MAPK-activated protein kinase activation. In the MAPK pathway responsible for cell growth, ERK2 initiates the first phosphorylation event on RSK1, which is inhibited by Ca(2+)-binding S100 proteins in malignant melanomas. Here, we present a detailed in vitro biochemical and structural characterization of the S100B-RSK1 interaction. The Ca(2+)-dependent binding of S100B to the calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase (CaMK)-type domain of RSK1 is reminiscent of the better known binding of calmodulin to CaMKII. Although S100B-RSK1 and the calmodulin-CAMKII system are clearly distinct functionally, they demonstrate how unrelated intracellular Ca(2+)-binding proteins could influence the activity of the CaMK domain-containing protein kinases. Our crystallographic, small angle x-ray scattering, and NMR analysis revealed that S100B forms a "fuzzy" complex with RSK1 peptide ligands. Based on fast-kinetics experiments, we conclude that the binding involves both conformation selection and induced fit steps. Knowledge of the structural basis of this interaction could facilitate therapeutic targeting of melanomas.
Keywords: RSK; S100 proteins; calcium; crystal structure; extracellular-signal-regulated kinase (ERK); kinetics; melanoma; mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK); nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR); small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS).
© 2016 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures





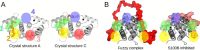
References
-
- Donato R. (2001) S100: a multigenic family of calcium-modulated proteins of the EF-hand type with intracellular and extracellular functional roles. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 33, 637–668 - PubMed
-
- Marenholz I., Heizmann C. W., and Fritz G. (2004) S100 proteins in mouse and man: from evolution to function and pathology (including an update of the nomenclature). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 322, 1111–1122 - PubMed
-
- Elliott P. R., Irvine A. F., Jung H. S., Tozawa K., Pastok M. W., Picone R., Badyal S. K., Basran J., Rudland P. S., Barraclough R., Lian L. Y., Bagshaw C. R., Kriajevska M., and Barsukov I. L. (2012) Asymmetric mode of Ca2+-S100A4 interaction with nonmuscle myosin IIA generates nanomolar affinity required for filament remodeling. Structure. 20, 654–666 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

