Phase II Study of Allogeneic Transplantation for Older Patients With Acute Myeloid Leukemia in First Complete Remission Using a Reduced-Intensity Conditioning Regimen: Results From Cancer and Leukemia Group B 100103 (Alliance for Clinical Trials in Oncology)/Blood and Marrow Transplant Clinical Trial Network 0502
- PMID: 26527780
- PMCID: PMC4658453
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.2015.62.7273
Phase II Study of Allogeneic Transplantation for Older Patients With Acute Myeloid Leukemia in First Complete Remission Using a Reduced-Intensity Conditioning Regimen: Results From Cancer and Leukemia Group B 100103 (Alliance for Clinical Trials in Oncology)/Blood and Marrow Transplant Clinical Trial Network 0502
Abstract
Purpose: Long-term survival rates for older patients with newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia (AML) are extremely low. Previous observational studies suggest that allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation (HSCT) may improve overall survival (OS) because of lower rates of relapse. We sought to prospectively determine the value of HSCT for older patients with AML in first complete remission.
Patients and methods: We conducted a prospective multicenter phase II study to assess the efficacy of reduced-intensity conditioning HSCT for patients between the ages of 60 and 74 years with AML in first complete remission. The primary end point was disease-free survival at 2 years after HSCT. Secondary end points included nonrelapse mortality (NRM), graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), relapse, and OS.
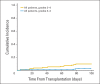
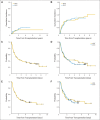
Results: In all, 114 patients with a median age of 65 years received transplantations. The majority (52%) received transplantations from unrelated donors and were given antithymocyte globulin for GVHD prophylaxis. Disease-free survival and OS at 2 years after transplantation were 42% (95% CI, 33% to 52%) and 48% (95% CI, 39% to 58%), respectively, for the entire group and 40% (95% CI, 29% to 55%) and 50% (95% CI, 38% to 64%) for the unrelated donor group. NRM at 2 years was 15% (95% CI, 8% to 21%). Grade 2 to 4 acute GVHD occurred in 9.6% (95% CI, 4% to 15%) of patients, and chronic GVHD occurred in 28% (95% CI, 19% to 36%) of patients. The cumulative incidence of relapse at 2 years was 44% (95% CI, 35% to 53%).
Conclusion: Reduced-intensity conditioning HSCT to maintain remission in selected older patients with AML is relatively well tolerated and appears to provide superior outcomes when compared with historical patients treated without HSCT. GVHD and NRM rates were lower than expected. Future transplantation studies in these patients should focus on further reducing the risk of relapse.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00070135.
© 2015 by American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors' disclosures of potential conflicts of interest are found in the article online at
Figures


References
-
- Rowe JM, Tallman MS. How I treat acute myeloid leukemia. Blood. 2010;116:3147–3156. - PubMed
-
- Goldstone AH, Burnett AK, Wheatley K, et al. Attempts to improve treatment outcomes in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in older patients: The results of the United Kingdom Medical Research Council AML11 trial. Blood. 2001;98:1302–1311. - PubMed
-
- Rowe JM, Neuberg D, Friedenberg W, et al. A phase 3 study of three induction regimens and of priming with GM-CSF in older adults with acute myeloid leukemia: A trial by the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. Blood. 2004;103:479–485. - PubMed
-
- Schoch C, Kern W, Schnittger S, et al. The influence of age on prognosis of de novo acute myeloid leukemia differs according to cytogenetic subgroups. Haematologica. 2004;89:1082–1090. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
- 1U10CA180836/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL069294/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 1U10CA180858/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 1U10CA180833/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA076518/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180821/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180858/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL069334/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180836/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL109137/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10CA180882/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180791/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180850/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 1U10CA180838/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 1U10CA180790/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180790/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 1U10CA180867/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180882/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10HL069294/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180833/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10CA180821/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 1U10CA180791/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180867/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180838/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 HL069315/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 1U10CA180850/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

