State of the art in the diagnosis and management of interstitial lung disease
- PMID: 26528058
- PMCID: PMC4576791
- DOI: 10.15386/cjmed-457
State of the art in the diagnosis and management of interstitial lung disease
Abstract
The interstitial lung diseases (ILDs) are a diverse group of disorders characterized by a varying combination of inflammation and fibrosis of the pulmonary parenchyma. Treatment and prognosis of ILD typically depend on the underlying ILD subtype, highlighting the importance of accurate classification and diagnosis. Besides a thorough history and clinical examination, the protocol should include a 6-minute walk test, chest radiography, high-resolution computed tomography, biochemical analysis, pulmonary function tests, blood gas analysis, bronchoalveolar lavage, and, when necessary, a lung biopsy. The final diagnosis of ILD entities requires dynamic interaction between clinicians, radiologists and pathologists to reach a clinico-radiologic-pathologic diagnosis, the gold standard no longer being the histology but rather a multidisciplinary approach.
Keywords: diagnosis; interstitial lung disease; nonspecific interstitial pneumonia; pulmonary fibrosis; usual interstitial pneumonia.
Figures
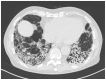
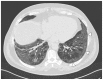
References
-
- Deconinck B, Verschakelen J, Coolen J, Verbeken E, Verleden G, Wuyts W. Diagnostic workup for diffuse parenchymal lung disease: schematic flowchart, literature review, and pitfalls. Lung. 2013;191(1):19–25. - PubMed
-
- Ryerson CJ, Collard HR. Update on the diagnosis and classification of ILD. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2013;19(5):453–459. - PubMed
-
- Larsen BT, Colby TV. Update for pathologists on idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2012;136(10):1234–1241. - PubMed
-
- American Thoracic Society, European Respiratory Society. American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society international multidisciplinary consensus classification of the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;165:277–304. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
