A Randomized Phase 2 Study Comparing 2 Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy Schedules for Medically Inoperable Patients With Stage I Peripheral Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: NRG Oncology RTOG 0915 (NCCTG N0927)
- PMID: 26530743
- PMCID: PMC4744654
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2015.07.2260
A Randomized Phase 2 Study Comparing 2 Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy Schedules for Medically Inoperable Patients With Stage I Peripheral Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: NRG Oncology RTOG 0915 (NCCTG N0927)
Erratum in
-
Erratum. A randomized phase 2 study comparing 2 stereotactic body radiation therapy schedules for medically inoperable patients with stage I peripheral non-small cell lung cancer: NRG Oncology RTOG 0915 (NCCTG N0927).Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2016 Mar 1;94(3):638. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2015.11.031. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2016. PMID: 26867895 No abstract available.
Abstract
Purpose: To compare 2 stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) schedules for medically inoperable early-stage lung cancer to determine which produces the lowest rate of grade ≥3 protocol-specified adverse events (psAEs) at 1 year.
Methods and materials: Patients with biopsy-proven peripheral (≥2 cm from the central bronchial tree) T1 or T2, N0 (clinically node negative by positron emission tomography), M0 tumors were eligible. Patients were randomized to receive either 34 Gy in 1 fraction (arm 1) or 48 Gy in 4 consecutive daily fractions (arm 2). Rigorous central accreditation and quality assurance confirmed treatment per protocol guidelines. This study was designed to detect a psAEs rate >17% at a 10% significance level (1-sided) and 90% power. Secondary endpoints included rates of primary tumor control (PC), overall survival (OS), and disease-free survival (DFS) at 1 year. Designating the better of the 2 regimens was based on prespecified rules of psAEs and PC for each arm.
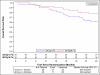
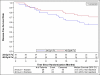
Results: Ninety-four patients were accrued between September 2009 and March 2011. The median follow-up time was 30.2 months. Of 84 analyzable patients, 39 were in arm 1 and 45 in arm 2. Patient and tumor characteristics were balanced between arms. Four (10.3%) patients on arm 1 (95% confidence interval [CI] 2.9%-24.2%) and 6 (13.3%) patients on arm 2 (95% CI 5.1%-26.8%) experienced psAEs. The 2-year OS rate was 61.3% (95% CI 44.2%-74.6%) for arm 1 patients and 77.7% (95% CI 62.5%-87.3%) for arm 2. The 2-year DFS was 56.4% (95% CI 39.6%-70.2%) for arm 1 and 71.1% (95% CI 55.5%-82.1%) for arm 2. The 1-year PC rate was 97.0% (95% CI 84.2%-99.9%) for arm 1 and 92.7% (95% CI 80.1%-98.5%) for arm 2.
Conclusions: 34 Gy in 1 fraction met the prespecified criteria and, of the 2 schedules, warrants further clinical research.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00960999.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Dose and Fractionation in Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy for Stage I Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Lessons Learned and Where Do We Go Next?Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2015 Nov 15;93(4):765-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2015.08.025. Epub 2015 Oct 19. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2015. PMID: 26530744 No abstract available.
References
-
- Uematsu M, Shioda A, Suda A, et al. Computed tomography-guided frameless stereotactic radiotherapy for stage I non-small cell lung cancer: a 5-year experience. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2001;51:666–670. - PubMed
-
- Nagata Y, Negoro Y, Aoki T, et al. Clinical outcomes of 3D conformal hypofractionated single high-dose radiotherapy for one or two lung tumors using a stereotactic body frame. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2002;52:1041–1046. - PubMed
-
- Wulf J, Baier K, Mueller G, et al. Dose-response in stereotactic irradiation of lung tumors. Radiother Oncol. 2005;77:83–87. - PubMed
-
- Baumann P, Nyman J, Lax I, et al. Factors important for efficacy of stereotactic body radiotherapy of medically inoperable stage I lung cancer. A retrospective analysis of patients treated in the Nordic countries. Acta Oncol. 2006;45:787–795. - PubMed
-
- Timmerman R, Papiez L, McGarry R, et al. Extracranial stereotactic radioablation: results of a phase I study in medically inoperable stage I non-small cell lung cancer. Chest. 2003;124:1946–1955. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous