Protein O-linked glycosylation in the plant pathogen Ralstonia solanacearum
- PMID: 26531228
- PMCID: PMC4736539
- DOI: 10.1093/glycob/cwv098
Protein O-linked glycosylation in the plant pathogen Ralstonia solanacearum
Abstract
Ralstonia solanacearum is one of the most lethal phytopathogens in the world. Due to its broad host range, it can cause wilting disease in many plant species of economic interest. In this work, we identified the O-oligosaccharyltransferase (O-OTase) responsible for protein O-glycosylation in R. solanacearum. An analysis of the glycoproteome revealed that 20 proteins, including type IV pilins are substrates of this general glycosylation system. Although multiple glycan forms were identified, the majority of the glycopeptides were modified with a pentasaccharide composed of HexNAc-(Pen)-dHex(3), similar to the O antigen subunit present in the lipopolysaccharide of multiple R. solanacearum strains. Disruption of the O-OTase led to the total loss of protein glycosylation, together with a defect in biofilm formation and reduced pathogenicity towards tomato plants. Comparative proteomic analysis revealed that the loss of glycosylation is not associated with widespread proteome changes. Only the levels of a single glycoprotein, the type IV pilin, were diminished in the absence of glycosylation. In parallel, disruption of glycosylation triggered an increase in the levels of a surface lectin homologous to Pseudomonas PA-IIL. These results reveal the important role of glycosylation in the pathogenesis of R. solanacearum.
Keywords: Type IV pili; biofilm; protein O-glycosylation.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures


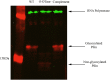
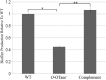

References
-
- Álvarez B, Biosca EG, López MM. 2010. On the life of Ralstonia solanacearum, a destructive bacterial plant pathogen. Current Research, Technology and Education Topics in Applied Microbiology and Microbial Biotechnology. 1:267–279.
-
- Anonsen JH, Vik A, Egge-Jacobsen W, Koomey M. 2012. An extended spectrum of target proteins and modification sites in the general O-linked protein glycosylation system in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. J Proteome Res. 11:5781–5793. - PubMed
-
- Araud-Razou I, Vasse J, Montrozier H, Etchebar C, Trigalet A. 1998. Detection and visualization of the major acidic exopolysaccharide of Ralstonia solanacearum and its role in tomato root infection and vascular colonization. Eur J Plant Pathol. 104:795–809.
-
- Balonova L, Mann BF, Cerveny L, Alley WR Jr, Chovancova E, Forslund AL, Salomonsson EN, Forsberg A, Damborsky J, Novotny MV et al. . 2012. Characterization of protein glycosylation in Francisella tularensis subsp. holarctica: identification of a novel glycosylated lipoprotein required for virulence. Mol Cell Proteomics. 11:M111 015016. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Boersema PJ, Raijmakers R, Lemeer S, Mohammed S, Heck AJ. 2009. Multiplex peptide stable isotope dimethyl labeling for quantitative proteomics. Nat Protoc. 4:484–494. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

