Estimating the monetary value of the annual productivity gained in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis receiving etanercept plus methotrexate: interim results from the PRIZE study
- PMID: 26535135
- PMCID: PMC4613161
- DOI: 10.1136/rmdopen-2014-000042
Estimating the monetary value of the annual productivity gained in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis receiving etanercept plus methotrexate: interim results from the PRIZE study
Abstract
Objective: To measure and value the impact of combined etanercept (ETN) and methotrexate (MTX) therapy on work productivity in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis (RA) over 52 weeks.
Methods: MTX- and biological-naïve patients with RA (symptom onset ≤12 months; Disease Activity Score based on a 28-joint count (DAS28) >3.2) received open-label ETN50/MTX for 52 weeks. The Valuation of Lost Productivity (VOLP) questionnaire, measuring paid and unpaid work productivity impacts, was completed approximately every 13 weeks. Bootstrapping methods were used to test changes in VOLP outcomes over time. One-year productivity impacts were compared between responders (DAS28 ≤3.2) at week 13 and non-responders using zero-inflated models for time loss and two-part models for total costs of lost productivity.
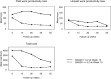
Results: 196 patients were employed at baseline and had ≥1 follow-up with VOLP. Compared with baseline, at week 52, patients gained 33.4 h per 3 months in paid work and 4.2 h per week in unpaid work. Total monetary productivity gains were €1322 per 3 months. Over the 1-year period, responders gained paid (231 h) and unpaid work loss (122 h) compared with non-responders, which amounted to a gain of €3670 for responders.
Conclusions: This is the first clinical trial to measure and value the impact of biological treatment on all the labour input components that affect overall productivity. Combination therapy with ETN50/MTX was associated with a significant productivity gain for patients with early RA who were still observed at week 52. Over the 1-year treatment period, responders at week 13 suffered significantly less productivity loss than non-responders suggesting this gain was related to treatment response.
Trial registration number: ClinicalTrials.gov number NCT00913458.
Keywords: DMARDs (biologic); Early Rheumatoid Arthritis; Economic Evaluations.
Figures
References
-
- Puolakka K, Kautiainen H, Möttönen T et al. . Impact of initial aggressive drug treatment with a combination of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs on the development of work disability in early rheumatoid arthritis: a five-year randomized followup trial. Arthritis Rheum 2004;50:55–62. 10.1002/art.11436 - DOI - PubMed
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical