Longitudinal evidence linking processing speed to the development of reasoning
- PMID: 26537631
- PMCID: PMC4860185
- DOI: 10.1111/desc.12352
Longitudinal evidence linking processing speed to the development of reasoning
Erratum in
-
Erratum.Dev Sci. 2018 Mar;21(2). doi: 10.1111/desc.12655. Dev Sci. 2018. PMID: 29521033 No abstract available.
Abstract
Age-related change in processing speed has been linked directly to increases in reasoning as well as indirectly via increases in the capacity of working memory (WM). Most of the evidence linking change in speed to reasoning has come from cross-sectional research; in this article we present the findings from a 2½-year longitudinal study of 277 6- to-13-year-olds. On three occasions, speed of information processing was assessed with Visual Matching and Cross Out; WM was assessed with reading, listening, backward digit, alphabet, and operation span tasks; and nonverbal reasoning was assessed with Raven's progressive matrices. The results provided consistent evidence of direct links from processing speed to reasoning but inconsistent evidence for indirect links from speed to WM to reasoning. These findings suggest that variations in processing speed may constrain the development of reasoning, directly and perhaps indirectly. A video abstract of this article can be viewed at: https://youtu.be/nc0VlFdi468.
© 2015 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
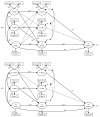
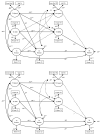
References
-
- Allen GL, Ondraceck PJ. Age-sensitive cognitive abilities related to children’s acquisition of spatial knowledge. Developmental Psychology. 1995;31:934–945. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/0012-1649.31.6.934. - DOI
-
- Daneman M, Carpenter PA. Individual differences in working memory and reading. Journal of Verbal Learning and Verbal Behavior. 1980;19:450–466. doi:10.1016/S0022-5371(80)90312-6.
-
- De Alwis D, Hale S, Myerson J. Extended cascade models of age and individual differences in children’s fluid intelligence. Intelligence. 2014;46:84–93. doi: 10.1016/j.intell.2014.05.008.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

