Losing women along the path to safe motherhood: why is there such a gap between women's use of antenatal care and skilled birth attendance? A mixed methods study in northern Uganda
- PMID: 26538084
- PMCID: PMC4632272
- DOI: 10.1186/s12884-015-0695-9
Losing women along the path to safe motherhood: why is there such a gap between women's use of antenatal care and skilled birth attendance? A mixed methods study in northern Uganda
Abstract
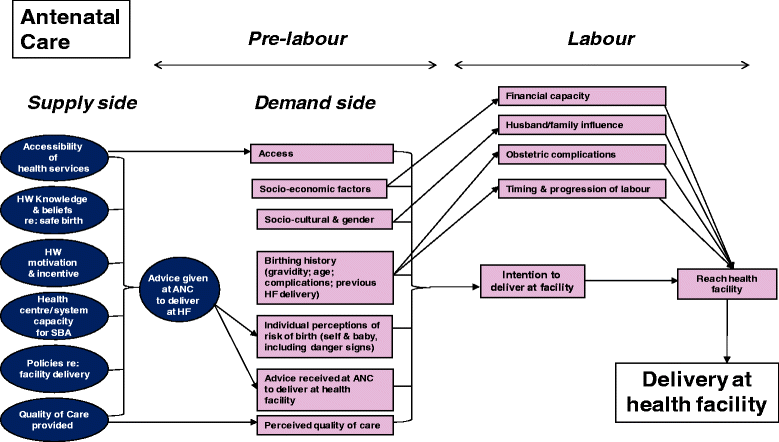
Background: Thousands of women and newborns still die preventable deaths from pregnancy and childbirth-related complications in poor settings. Delivery with a skilled birth attendant is a vital intervention for saving lives. Yet many women, particularly where maternal mortality ratios are highest, do not have a skilled birth attendant at delivery. In Uganda, only 58 % of women deliver in a health facility, despite approximately 95 % of women attending antenatal care (ANC). This study aimed to (1) identify key factors underlying the gap between high rates of antenatal care attendance and much lower rates of health-facility delivery; (2) examine the association between advice during antenatal care to deliver at a health facility and actual place of delivery; (3) investigate whether antenatal care services in a post-conflict district of Northern Uganda actively link women to skilled birth attendant services; and (4) make recommendations for policy- and program-relevant implementation research to enhance use of skilled birth attendance services.
Methods: This study was carried out in Gulu District in 2009. Quantitative and qualitative methods used included: structured antenatal care client entry and exit interviews [n = 139]; semi-structured interviews with women in their homes [n = 36], with health workers [n = 10], and with policymakers [n = 10]; and focus group discussions with women [n = 20], men [n = 20], and traditional birth attendants [n = 20].
Results: Seventy-five percent of antenatal care clients currently pregnant reported they received advice during their last pregnancy to deliver in a health facility, and 58 % of these reported having delivered in a health facility. After adjustment for confounding, women who reported they received advice at antenatal care to deliver at a health facility were significantly more likely (aOR = 2.83 [95 % CI: 1.19-6.75], p = 0.02) to report giving birth in a facility. Despite high antenatal care coverage, a number of demand and supply side barriers deter use of skilled birth attendance services. Primary barriers were: fear of being neglected or maltreated by health workers; long distance and other difficulties in access; poverty, and material requirements for delivery; lack of support from husband/partner; health systems deficiencies such as inadequate staffing/training, work environment, and referral systems; and socio-cultural and gender issues such as preferred birthing position and preference for traditional birth attendants.
Conclusions: Initiatives to improve quality of client-provider interaction and respect for women are essential. Financial barriers must be abolished and emergency transport for referrals improved. Simultaneously, supply-side barriers must be addressed, notably ensuring a sufficient number of health workers providing skilled obstetric care in health facilities and creating habitable conditions and enabling environments for them.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. Why do so many women still die in pregnancy or childbirth? 2013. http://www.who.int/features/qa/12/en/ [Accessed 09 September 2013].
-
- World Health Organization . Reduction of Maternal Mortality: A Joint WHO/UNFPA/UNICEF/World Bank Statement. Geneva: World Health Organization; 1999.
-
- World Health Organization . Trends in maternal mortality: 1990 to 2010. WHO, UNICEF, UNFPA, and The World Bank estimates. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2010. p. 2012.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous