The role of osteoclast differentiation and function in skeletal homeostasis
- PMID: 26538571
- PMCID: PMC4882648
- DOI: 10.1093/jb/mvv112
The role of osteoclast differentiation and function in skeletal homeostasis
Abstract
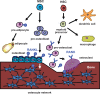
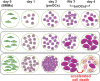
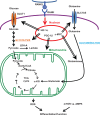
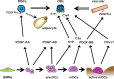
Osteoclasts are giant multinucleated cells that differentiate from hematopoietic cells in the bone marrow and carry out important physiological functions in the regulation of skeletal homeostasis as well as hematopoiesis. Osteoclast biology shares many features and components with cells of the immune system, including cytokine-receptor interactions (RANKL-RANK), intracellular signalling molecules (TRAF6) and transcription factors (NFATc1). Although the roles of these molecules in osteoclast differentiation are well known, fundamental questions remain unsolved, including the exact location of the RANKL-RANK interaction and the in vivo temporal and spatial information on the transformation of hematopoietic cells into bone-resorbing osteoclasts. This review focuses on the importance of cell-cell contact and metabolic adaptation for differentiation, relatively overlooked aspects of osteoclast biology and biochemistry.
Keywords: PGC-1β; glutaminolysis; glycolysis; iron; mitochondria.
© The Authors 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Japanese Biochemical Society. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Erlebacher A., Filvaroff E.H., Gitelman S.E., Derynck R. (1995) Toward a molecular understanding of skeletal development. Cell 80, 371–378 - PubMed
-
- Kronenberg H.M. (2003) Developmental regulation of the growth plate. Nature 423, 332–336 - PubMed
-
- Zaidi M. (2007) Skeletal remodeling in health and disease. Nat. Med. 13, 791–801 - PubMed
-
- Teitelbaum S.L. (2000) Bone resorption by osteoclasts. Science (New York, N.Y.) 289, 1504–1508 - PubMed
-
- Teitelbaum S.L., Ross F.P. (2003) Genetic regulation of osteoclast development and function. Nat. Rev. Genet. 4, 638–649 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

