A memristive spiking neuron with firing rate coding
- PMID: 26539074
- PMCID: PMC4611138
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2015.00376
A memristive spiking neuron with firing rate coding
Abstract
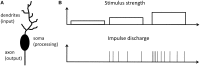
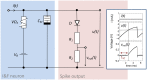
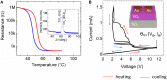
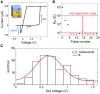
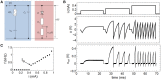
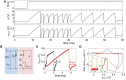
Perception, decisions, and sensations are all encoded into trains of action potentials in the brain. The relation between stimulus strength and all-or-nothing spiking of neurons is widely believed to be the basis of this coding. This initiated the development of spiking neuron models; one of today's most powerful conceptual tool for the analysis and emulation of neural dynamics. The success of electronic circuit models and their physical realization within silicon field-effect transistor circuits lead to elegant technical approaches. Recently, the spectrum of electronic devices for neural computing has been extended by memristive devices, mainly used to emulate static synaptic functionality. Their capabilities for emulations of neural activity were recently demonstrated using a memristive neuristor circuit, while a memristive neuron circuit has so far been elusive. Here, a spiking neuron model is experimentally realized in a compact circuit comprising memristive and memcapacitive devices based on the strongly correlated electron material vanadium dioxide (VO2) and on the chemical electromigration cell Ag/TiO2-x /Al. The circuit can emulate dynamical spiking patterns in response to an external stimulus including adaptation, which is at the heart of firing rate coding as first observed by E.D. Adrian in 1926.
Keywords: memristive devices; negative differential resistor; neural coding; neuromorphic systems; spiking neuron.
Figures

References
-
- Adrian E. D. (1928). The Basis of Sensation. New York, NY: W. W. Norton.
-
- Andersson G. (1956). Studies on vanadium oxides. II. The crystal structure of vanadium dioxide. Acta Chem. Scand. 10, 623–628. 10.3891/acta.chem.scand.10-0623 - DOI
-
- Barlow H. (1961). Possible principles underlying the transformation of sensory messages, in Sensory Communication, ed Rosenblith W. (Cambridge, MA: MIT Press; ), 217–234.
-
- Bear M. F., Connors B. W., Paradiso M. A. (2006). Neuroscience: Exploring the Brain. Hagerstown, MD: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

