A Comparison of Variant Calling Pipelines Using Genome in a Bottle as a Reference
- PMID: 26539496
- PMCID: PMC4619817
- DOI: 10.1155/2015/456479
A Comparison of Variant Calling Pipelines Using Genome in a Bottle as a Reference
Abstract
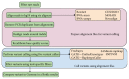
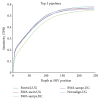
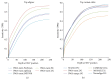
High-throughput sequencing, especially of exomes, is a popular diagnostic tool, but it is difficult to determine which tools are the best at analyzing this data. In this study, we use the NIST Genome in a Bottle results as a novel resource for validation of our exome analysis pipeline. We use six different aligners and five different variant callers to determine which pipeline, of the 30 total, performs the best on a human exome that was used to help generate the list of variants detected by the Genome in a Bottle Consortium. Of these 30 pipelines, we found that Novoalign in conjunction with GATK UnifiedGenotyper exhibited the highest sensitivity while maintaining a low number of false positives for SNVs. However, it is apparent that indels are still difficult for any pipeline to handle with none of the tools achieving an average sensitivity higher than 33% or a Positive Predictive Value (PPV) higher than 53%. Lastly, as expected, it was found that aligners can play as vital a role in variant detection as variant callers themselves.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

