Host-Targeting Agents to Prevent and Cure Hepatitis C Virus Infection
- PMID: 26540069
- PMCID: PMC4664971
- DOI: 10.3390/v7112898
Host-Targeting Agents to Prevent and Cure Hepatitis C Virus Infection
Abstract
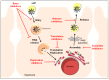
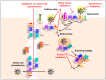
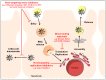
Chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is a major cause of liver cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) which are leading indications of liver transplantation (LT). To date, there is no vaccine to prevent HCV infection and LT is invariably followed by infection of the liver graft. Within the past years, direct-acting antivirals (DAAs) have had a major impact on the management of chronic hepatitis C, which has become a curable disease in the majority of DAA-treated patients. In contrast to DAAs that target viral proteins, host-targeting agents (HTAs) interfere with cellular factors involved in the viral life cycle. By acting through a complementary mechanism of action and by exhibiting a generally higher barrier to resistance, HTAs offer a prospective option to prevent and treat viral resistance. Indeed, given their complementary mechanism of action, HTAs and DAAs can act in a synergistic manner to reduce viral loads. This review summarizes the different classes of HTAs against HCV infection that are in preclinical or clinical development and highlights their potential to prevent HCV infection, e.g., following LT, and to tailor combination treatments to cure chronic HCV infection.
Keywords: direct-acting antiviral; hepatitis C virus; host-targeting agent; viral resistance.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Addressing the Challenges of Hepatitis C Virus Resistance and Treatment Failure.Viruses. 2016 Aug 16;8(8):226. doi: 10.3390/v8080226. Viruses. 2016. PMID: 27537906 Free PMC article.
-
Host-targeting agents for prevention and treatment of chronic hepatitis C - perspectives and challenges.J Hepatol. 2013 Feb;58(2):375-84. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2012.09.022. Epub 2012 Oct 4. J Hepatol. 2013. PMID: 23041307 Review.
-
Avasimibe: A novel hepatitis C virus inhibitor that targets the assembly of infectious viral particles.Antiviral Res. 2017 Dec;148:5-14. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2017.10.016. Epub 2017 Oct 23. Antiviral Res. 2017. PMID: 29074218
-
Therapy of chronic hepatitis C virus infection in the era of direct-acting and host-targeting antiviral agents.J Infect. 2014 Jan;68(1):1-20. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2013.08.019. Epub 2013 Sep 4. J Infect. 2014. PMID: 24012819 Review.
-
The history of hepatitis C virus (HCV): Basic research reveals unique features in phylogeny, evolution and the viral life cycle with new perspectives for epidemic control.J Hepatol. 2016 Oct;65(1 Suppl):S2-S21. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2016.07.035. J Hepatol. 2016. PMID: 27641985 Review.
Cited by
-
Overview of HCV Life Cycle with a Special Focus on Current and Possible Future Antiviral Targets.Viruses. 2019 Jan 6;11(1):30. doi: 10.3390/v11010030. Viruses. 2019. PMID: 30621318 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical development of hepatitis C virus host-targeting agents.Lancet. 2017 Feb 18;389(10070):674-675. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)30043-0. Epub 2017 Jan 11. Lancet. 2017. PMID: 28087068 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Human enterovirus 71 protein interaction network prompts antiviral drug repositioning.Sci Rep. 2017 Feb 21;7:43143. doi: 10.1038/srep43143. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28220872 Free PMC article.
-
Alkaloid and benzopyran compounds of Melicope latifolia fruit exhibit anti-hepatitis C virus activities.BMC Complement Med Ther. 2021 Jan 12;21(1):27. doi: 10.1186/s12906-021-03202-8. BMC Complement Med Ther. 2021. PMID: 33435968 Free PMC article.
-
Addressing the Challenges of Hepatitis C Virus Resistance and Treatment Failure.Viruses. 2016 Aug 16;8(8):226. doi: 10.3390/v8080226. Viruses. 2016. PMID: 27537906 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lindenbach B.D., Thiel H.J., Rice C.M. Flaviviridae: The viruses and their replication. In: Knipe D.M., Howley P.M., editors. Fields Virology. Lippincott-Raven; Philadelphia, PA, USA: 2007. pp. 1101–1152.
-
- Steinmann E., Pietschmann T. Cell culture systems for hepatitis C virus. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2013;369:17–48. - PubMed
-
- Billerbeck E., de Jong Y., Dorner M., de la Fuente C., Ploss A. Animal models for hepatitis C. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2013;369:49–86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

