Role of Matrix Metalloproteinases in the Pathogenesis of Traumatic Brain Injury
- PMID: 26541883
- PMCID: PMC9470225
- DOI: 10.1007/s12035-015-9520-8
Role of Matrix Metalloproteinases in the Pathogenesis of Traumatic Brain Injury
Abstract
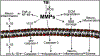
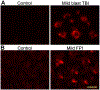
Traumatic brain injury (TBI) is a major cause of mortality and morbidity worldwide. Studies revealed that the pathogenesis of TBI involves upregulation of MMPs. MMPs form a large family of closely related zinc-dependent endopeptidases, which are primarily responsible for the dynamic remodulation of the extracellular matrix (ECM). Thus, they are involved in several normal physiological processes like growth, development, and wound healing. During pathophysiological conditions, MMPs proteolytically degrade various components of ECM and tight junction (TJ) proteins of BBB and cause BBB disruption. Impairment of BBB causes leakiness of the blood from circulation to brain parenchyma that leads to microhemorrhage and edema. Further, MMPs dysregulate various normal physiological processes like angiogenesis and neurogenesis, and also they participate in the inflammatory and apoptotic cascades by inducing or regulating the specific mediators and their receptors. In this review, we explore the roles of MMPs in various physiological/pathophysiological processes associated with neurological complications, with special emphasis on TBI.
Keywords: Blood-brain barrier; Edema; Extracellular matrix; Hemorrhage; Matrix metalloproteinases; Neurodegeneration; Neuroinflammation; Traumatic brain injury.
Figures
References
-
- Nagase H, Woessner JF Jr (1999) Matrix metalloproteinases. J Biol Chem 274:21491–21494 - PubMed
-
- Yong VW (2005) Metalloproteinases: mediators of pathology and regeneration in the CNS. Nat Rev Neurosci 6:931–944 - PubMed
-
- Engel CK, Pirard B, Schimanski S, Kirsch R, Habermann J, Klingler O, Schlotte V, Weithmann KU et al. (2005) Structural basis for the highly selective inhibition of MMP-13. Chem Biol 12:181–189 - PubMed
-
- Visse R, Nagase H (2003) Matrix metalloproteinases and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases: structure, function, and biochemistry. Circ Res 92:827–839 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

