Inflammatory pseudotumor of the hip: a complication of arthroplasty to be recognized by the radiologist
- PMID: 26543283
- PMCID: PMC4633076
- DOI: 10.1590/0100-3984.2013.0005
Inflammatory pseudotumor of the hip: a complication of arthroplasty to be recognized by the radiologist
Abstract
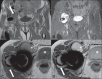
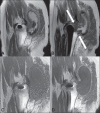
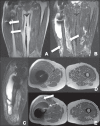
Soft tissue complications following hip arthroplasty may occur either in cases of total hip arthroplasty or in hip resurfacing, a technique that has become popular in cases involving young patients. Both orthopedic and radiological literatures are now calling attention to these symptomatic periprosthetic soft tissue masses called inflammatory pseudotumors or aseptic lymphocytic vasculites-associated lesions. Pseudotumors are associated with pain, instability, neuropathy, and premature loosening of prosthetic components, frequently requiring early and difficult reoperation. Magnetic resonance imaging plays a relevant role in the evaluation of soft tissue changes in the painful hip after arthroplasty, ranging from early periprosthetic fluid collections to necrosis and more extensive tissue damage.
Complicações em partes moles pós-artroplastia do quadril são suscetíveis de ocorrer, seja quando da artroplastia total, seja quando se utiliza a técnica de recapeamento da cabeça femoral, opção que se tornou popular em casos de pacientes jovens. Tanto a literatura ortopédica quanto a radiológica têm chamado a atenção para massas “sintomáticas” que surgem em partes moles adjacentes a próteses, denominadas pseudotumores inflamatórios ou lesões associadas a vasculite linfocítica asséptica. Os pseudotumores estão associados a dor, instabilidade, neuropatia e afrouxamento prematuro dos componentes da prótese, geralmente levando a cirurgias de revisão precoces e difíceis. A ressonância magnética tem papel muito importante na avaliação das alterações em partes moles do quadril doloroso pós-artroplastia, que variam desde coleções fluidas periprotéticas precoces até necrose e dano tecidual mais extenso.
Keywords: Hip arthroplasty; Inflammatory pseudotumor of the hip; Magnetic resonance imaging.
Figures

References
-
- Walsh AJ, Nikolaou VS, Antoniou J. Inflammatory pseudotumor complicating metal-on-highly cross-linked polyethylene total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2012;27:324.e5–324.e8. - PubMed
-
- Mao X, Tay GH, Godbolt DB, et al. Pseudotumor in a well-fixed metal-on-polyethylene uncemented hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2012;27:493.e13–493.e17. - PubMed
-
- Murgatroyd SE. Pseudotumor presenting as a pelvic mass: a complication of eccentric wear of a metal on polyethylene hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2012;27:820.e1–820.e4. - PubMed
-
- Bestic JM, Berquist TH. Current concepts in hip arthroplasty imaging: metal-on-metal prostheses, their complications, and imaging strategies. Semin Roentgenol. 2013;48:178–186. - PubMed
-
- Ostlere S. How to image metal-on-metal prostheses and their complications. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011;197:558–567. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
